Deques: A Simple Example
This is a simple example of the Bridge Pattern meant only to show how it works.
Recall that a Deque (Doubly Ended QUEue) is a list that provides operations for getting, adding, and removing the first and last items. Stack and Queue are special cases of a Deque.
We can implement the Deque operations by delegating to a peer that implements the List operations. These operations allow users to get, add, and remove items at any position. A list can be implemented as an array or a linked list:
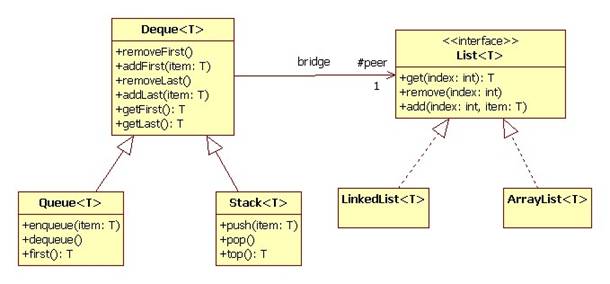
Here is how the Deque class might look in Java:
class Deque<T> {
protected List<T> peer; // =
linked list, array list, ...
public void addFirst(T item) {
peer.add(0, item);
}
// etc.
}
Here's the Stack class:
class Stack<T> extends Deque<T> {
public void push(T item) {
addFirst(item);
}
// etc.
}