JUnit
JUnit is a framework for unit testing. Here's its basic design:
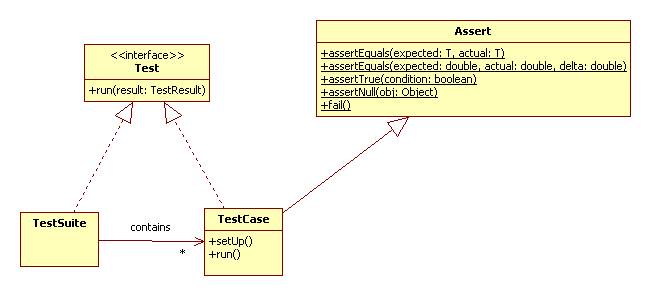
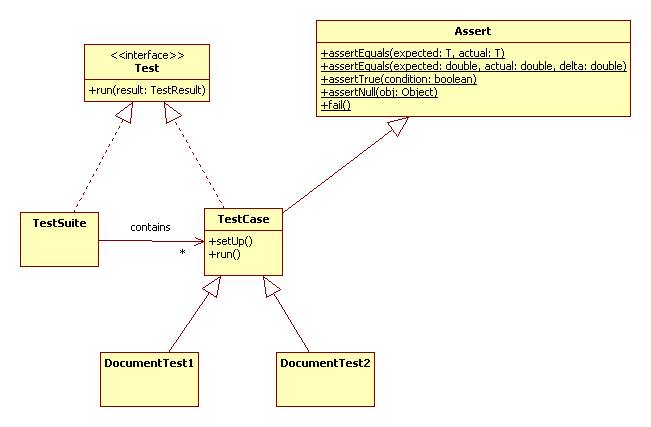
Every class should have a test case or several test cases grouped into a test suite.
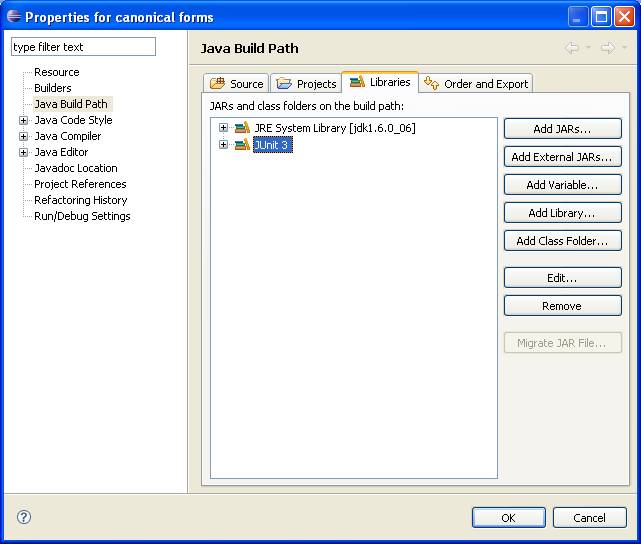
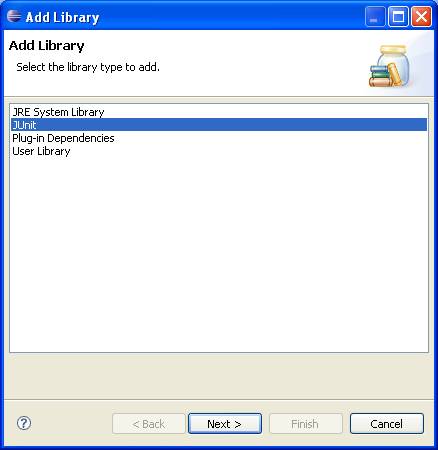
Before we begin, we must add the JUnit library to our project:
Next, we use the New JUnit Test Case to add a new test case for the Document class:
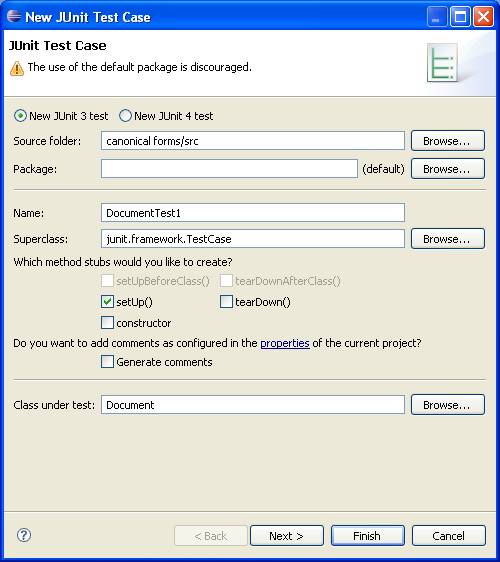
In the next dialog we specify which Document methods should be tested:

Here's our implementation:
import
junit.framework.TestCase;
public class
DocumentTest1 extends TestCase {
// fixture
private
Document doc;
protected
void setUp() throws Exception {
super.setUp();
doc
= new Document("Title1");
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
doc.add("word_" + i);
}
}
public
void testGetTitle() {
assertEquals(doc.getTitle(), "Title1");
}
public
void testAdd() {
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
doc.add("word_" + i + 100);
}
assertEquals(doc.size(), 110);
}
public
void testRemove() {
for(int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
doc.remove("word_" + i + 50);
}
}
}
Here's a screen shot of the JUnit tab with its comforting green bar:
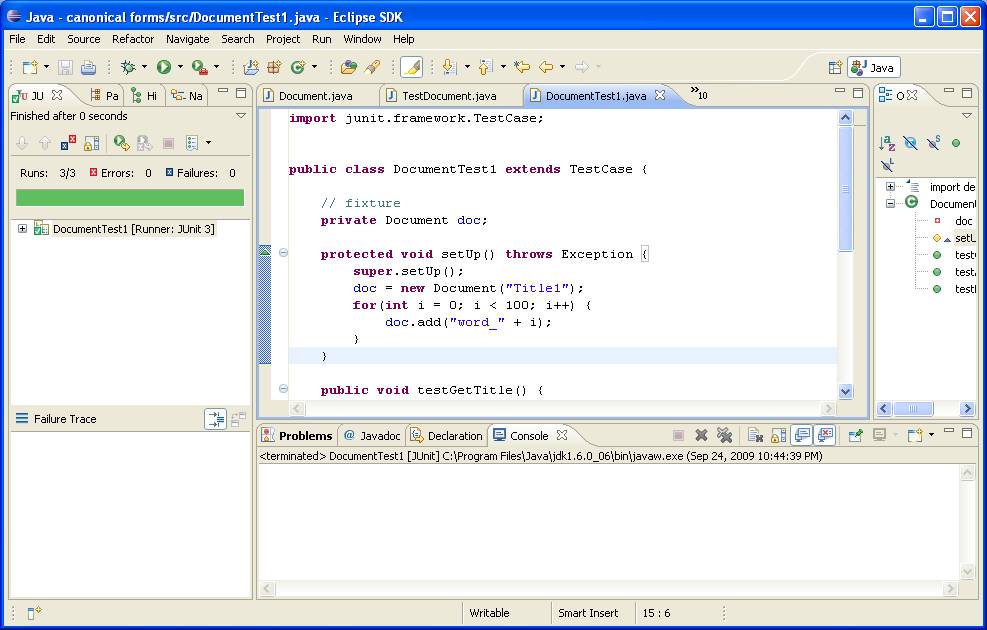
Here's a second test case:
public class
DocumentTest2 extends TestCase {
// fixture
private Document doc;
protected void setUp() throws Exception {
super.setUp();
doc = new Document("Title1");
for(int i = 0; i <
100; i++) {
doc.add("word_" + i);
}
}
public void testIterator()
{
int i = 0;
Iterator<String>
p = doc.iterator();
while(p.hasNext()) {
assertEquals(p.next(),
"word_" + i++);
}
}
}
We can run these together by putting them in a test suite.
First we create the suite:
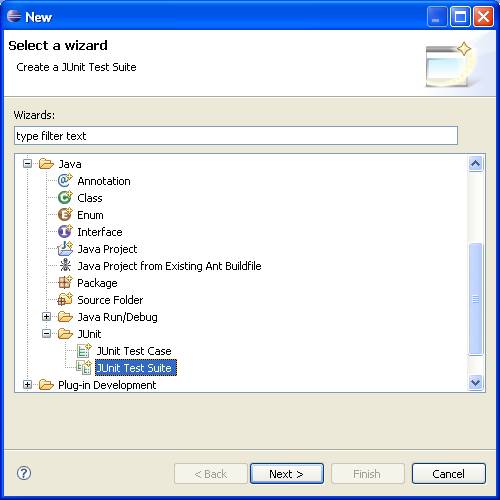
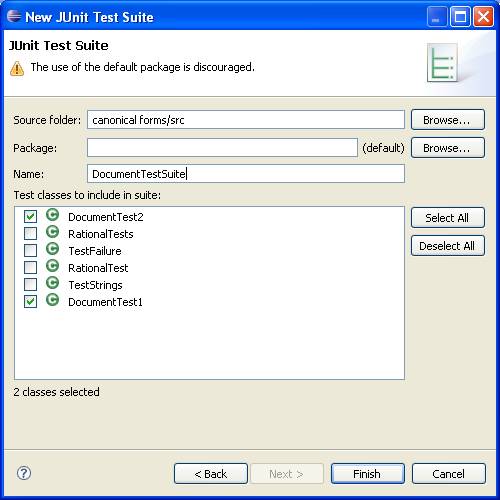
Here's the code generated:
public class
DocumentTestSuite {
public static Test suite()
{
TestSuite suite
= new
TestSuite("Test for default
package");
//$JUnit-BEGIN$
suite.addTestSuite(DocumentTest2.class);
suite.addTestSuite(DocumentTest1.class);
//$JUnit-END$
return suite;
}
}