Containers
A container is an object that contains 0 or more other objects.
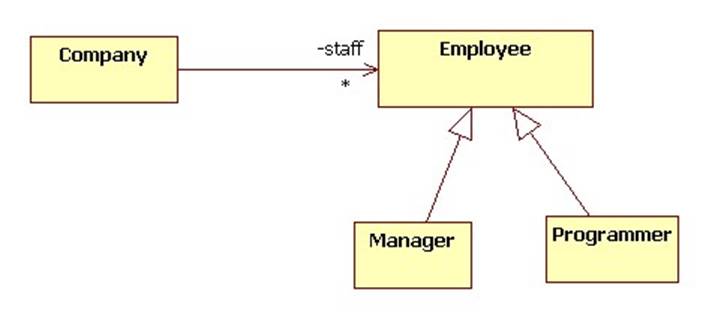
The container manages a collection such as a set, list, or array:
class Company {
private List<Employee> staff =
new ArrayList<Employee>();
public void hire(Employee e) {
staff.add(e);
}
public void fire(Employee e) {
staff.remove(e);
}
public int find(Employee e) {
return staff.indexOf(e);
}
public Employee get(int i) {
return staff.get(i);
}
public int size() {
return staff.size();
}
}
Note the management methods provided by the container include methods for adding, removing, and fetching members.
Here's a text harness:
class TestCompany {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Company acme = new Company();
acme.hire(new Manager());
acme.hire(new Programmer());
acme.hire(new Employee());
for(int i = 0; i < acme.size();
i++) {
acme.get(i).getToWork();
}
}
}
Here's the output produced:
fire somebody
fix bugs
look busy