Overview of
Software Engineering
Concepts
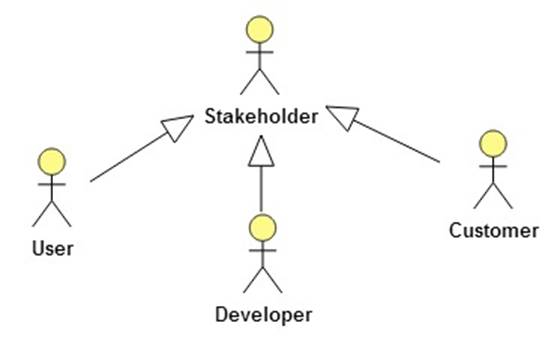
Stakeholders
Anyone with an interest in the outcome of a project is called a stakeholder.
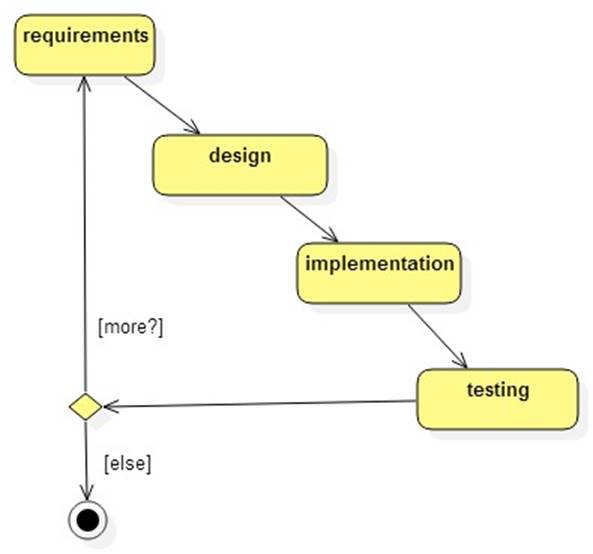
Lifecycle Models
Modern software development lifecycle models are iterative and include at least four major activities (from the 1997 IEEE 1074 Framework):
Classifying Lifecycle Models
Lifecycle models are divided into
activity-centered models and entity-centered models.
Activity-centered models focus on
processes. Entity-centered models focus on work products.
Lifecycle models can be sequential or
iterative.
Lifecycle models can have maturity levels.
The CMM framework
identifies five maturity levels for a software lifecycle:
Initial
Repeatable
Defined
Managed
Optimized
Lifecycle models can be placed on a
spectrum:

Adaptive models can quickly react to
requirement changes, but can't often predict where they will be in six months.
Planning, controlling, big up-front design, documenting, and monitoring are
hallmarks of predictive models.
Agile methodologies dominate the adaptive
end of the spectrum, while heavyweight processes like RUP and Waterfall
dominate the predictive end of the spectrum.
Examples of Lifecycle Models
Functional
Specification (Requirements + Analysis Model)
A model of the system from the user's perspective.
Design Model
A model of the system from the developer's perspective.
Older Lectures
http://www.cs.sjsu.edu/faculty/pearce/modules/lectures/se