










Sensors, OpenGL iPhone
CS185c
Chris Pollett
Nov. 17, 2010











CS185c
Chris Pollett
Nov. 17, 2010
- (void) locationManager: (CLLocationManager *)manager didUpdateToLocation: (CLLocation *)newLocation fromLocation: (CLLocation *)oldLocation ; - (void) locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didUpdateHeading: (CLHeading *)newHeading ; - (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didFailWithError:(NSError *)error ;to handle location and heading info, we implement the interface CLLocationManagerDelegate; to promise that our controller has methods
- (void)accelerometer:(UIAccelerometer *)accelerometer didAccelerate:(UIAcceleration *)acceleration;to handle accelerometer info, we implement the interface UIAccelerometerDelegate.
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
#import <CoreLocation/CoreLocation.h>
@interface SensorTestsViewController : UIViewController <CLLocationManagerDelegate,
UIAccelerometerDelegate> {
IBOutlet UILabel *locationLabel;
IBOutlet UILabel *headingLabel;
IBOutlet UILabel *accelerometerLabel;
CLLocationManager *locationManager;
}
@property (retain, nonatomic) UILabel *locationLabel;
@property (retain, nonatomic) UILabel *headingLabel;
@property (retain, nonatomic) UILabel *accelerometerLabel;
@end

#import "SensorTestsViewController.h"
@implementation SensorTestsViewController
@synthesize locationLabel;
@synthesize headingLabel;
@synthesize accelerometerLabel;
- (void) viewDidLoad {
locationManager = [[CLLocationManager alloc] init];
locationManager.delegate = self;
locationManager.desiredAccuracy = kCLLocationAccuracyBest;
[locationManager startUpdatingLocation];
[locationManager startUpdatingHeading];
UIAccelerometer *accelerometer = [UIAccelerometer sharedAccelerometer];
accelerometer.delegate = self;
accelerometer.updateInterval = 1.0f/60.0f; /* how many times a second to send
acclerometer updates. Shouldn't do too fast or battery dies. */
}
- (void) locationManager: (CLLocationManager *)manager
didUpdateToLocation: (CLLocation *)newLocation fromLocation: (CLLocation *)oldLocation {
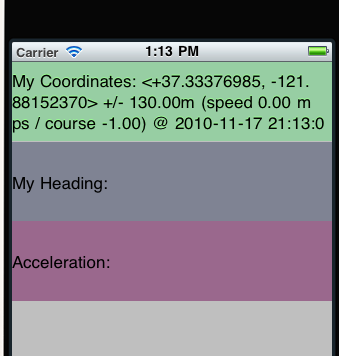
NSString *loc = [[NSString alloc] initWithFormat:@"My Coordinates: %@",
newLocation.description];
locationLabel.text = loc;
[loc release];
}
- (void) locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager
didUpdateHeading: (CLHeading *)newHeading {
NSString *head = [[NSString alloc] initWithFormat:@"My Heading: %@",
newHeading.description];
headingLabel.text = head;
[head release];
}
- (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didFailWithError:(NSError *)error {
if ([error code] == kCLErrorDenied) {
[locationManager stopUpdatingLocation];
}
}
- (void)accelerometer:(UIAccelerometer *)accelerometer
didAccelerate:(UIAcceleration *)acceleration {
NSString *head = [[NSString alloc] initWithFormat:@"Acceleration: X:%f Y:%f Z:%f",
acceleration.x, acceleration.y, acceleration.z];
accelerometerLabel.text = head;
[head release];
}
- (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning {
// Releases the view if it doesn't have a superview.
[super didReceiveMemoryWarning];
}
- (void)viewDidUnload {
}
- (void)dealloc {
[locationLabel release];
[locationManager release];
[super dealloc];
}
@end
string.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<string name="xyz">Acceleration: X: Y: Z:</string>
<string name="app_name">AccelerometerDemo</string>
</resources>
main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/xyz"
android:id="@+id/acceleration"
/>
</LinearLayout>
public void onSensorChanged(SensorEvent event);
public void onAccuracyChanged(Sensor arg0, int arg1);
We really only care about code in the former method.
package org.pollett;
import java.util.List;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.hardware.Sensor;
import android.hardware.SensorEvent;
import android.hardware.SensorEventListener;
import android.hardware.SensorManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class AccelerometerDemo extends Activity implements SensorEventListener
{
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
accelerationLabel = (TextView )this.findViewById(R.id.acceleration);
manager = (SensorManager)getSystemService(SENSOR_SERVICE);
List<Sensor> list = manager.getSensorList(Sensor.TYPE_ACCELEROMETER);
if(list != null && list.size() > 0) {
accelerometer = list.get(0);
}
}
@Override
public void onResume()
{
super.onResume();
if(accelerometer != null)
{
manager.registerListener(this,
accelerometer, SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_NORMAL);
}
}
@Override
public void onPause()
{
super.onPause();
if(accelerometer != null)
{
manager.unregisterListener(this);
}
}
public void onAccuracyChanged(Sensor arg0, int arg1) {
}
public void onSensorChanged(SensorEvent event) {
accelerationLabel.setText("Acceleration X:" + event.values[0]
+ " Y:" + event.values[1]
+ " Z:" + event.values[2]);
}
protected TextView accelerationLabel;
protected SensorManager manager;
protected Sensor accelerometer;
}
[glView startAnimation];in appDidFinishLaunching
renderer = [[ES2Renderer alloc] init];
- (void) startAnimation
{
if (!animating)
{
if (displayLinkSupported)
{
// CADisplayLink is API new to iPhone SDK 3.1. Compiling against earlier versions will result in a warning, but can be dismissed
// if the system version runtime check for CADisplayLink exists in -initWithCoder:. The runtime check ensures this code will
// not be called in system versions earlier than 3.1.
displayLink = [NSClassFromString(@"CADisplayLink") displayLinkWithTarget:self selector:@selector(drawView:)];
[displayLink setFrameInterval:animationFrameInterval];
[displayLink addToRunLoop:[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];
}
else
animationTimer = [NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:(NSTimeInterval)((1.0 / 60.0) * animationFrameInterval) target:self selector:@selector(drawView:) userInfo:nil repeats:TRUE];
animating = TRUE;
}
}
- (void) drawView:(id)sender
{
[renderer render];
}
// Create an ES 2.0 context
- (id) init
{
if (self = [super init])
{
context = [[EAGLContext alloc] initWithAPI:kEAGLRenderingAPIOpenGLES2];
if (!context || ![EAGLContext setCurrentContext:context] || ![self loadShaders])
{
[self release];
return nil;
}
// Create default framebuffer object. The backing will be allocated for the current layer in -resizeFromLayer
glGenFramebuffers(1, &defaultFramebuffer);
glGenRenderbuffers(1, &colorRenderbuffer);
glBindFramebuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, defaultFramebuffer);
glBindRenderbuffer(GL_RENDERBUFFER, colorRenderbuffer);
glFramebufferRenderbuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT0, GL_RENDERBUFFER, colorRenderbuffer);
}
return self;
}
The code to render things should look reasonably familiar if you followed the Android examples...
- (void) render
{
// Replace the implementation of this method to do your own custom drawing
static const GLfloat squareVertices[] = {
-0.5f, -0.33f,
0.5f, -0.33f,
-0.5f, 0.33f,
0.5f, 0.33f,
};
static const GLubyte squareColors[] = {
255, 255, 0, 255,
0, 255, 255, 255,
0, 0, 0, 0,
255, 0, 255, 255,
};
static float transY = 0.0f;
// This application only creates a single context which is already set current at this point.
// This call is redundant, but needed if dealing with multiple contexts.
[EAGLContext setCurrentContext:context];
// This application only creates a single default framebuffer which is already bound at this point.
// This call is redundant, but needed if dealing with multiple framebuffers.
glBindFramebuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, defaultFramebuffer);
glViewport(0, 0, backingWidth, backingHeight);
glClearColor(0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// Use shader program
glUseProgram(program);
// Update uniform value
glUniform1f(uniforms[UNIFORM_TRANSLATE], (GLfloat)transY);
transY += 0.075f;
// Update attribute values
glVertexAttribPointer(ATTRIB_VERTEX, 2, GL_FLOAT, 0, 0, squareVertices);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(ATTRIB_VERTEX);
glVertexAttribPointer(ATTRIB_COLOR, 4, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, 1, 0, squareColors);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(ATTRIB_COLOR);
// Validate program before drawing. This is a good check, but only really necessary in a debug build.
// DEBUG macro must be defined in your debug configurations if that's not already the case.
#if defined(DEBUG)
if (![self validateProgram:program])
{
NSLog(@"Failed to validate program: %d", program);
return;
}
#endif
// Draw
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP, 0, 4);
// This application only creates a single color renderbuffer which is already bound at this point.
// This call is redundant, but needed if dealing with multiple renderbuffers.
glBindRenderbuffer(GL_RENDERBUFFER, colorRenderbuffer);
[context presentRenderbuffer:GL_RENDERBUFFER];
}
glViewport(0, 0, backingWidth, backingHeight);corresponds to the code we had in our Android application
gl.glViewport(0, 0, view.getWidth(), view.getHeight());