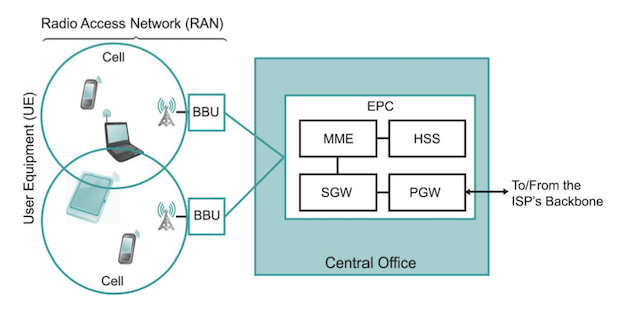
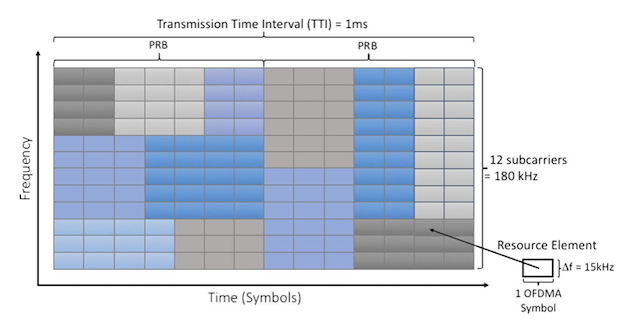
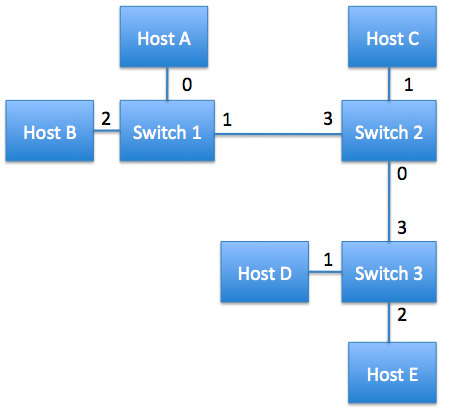
Generations Cell Technologies (1-3)
There have been several different generations of cell phone technologies:
- (1G) was analog and didn't support data communications to any degree (it did have something later called D-AMPS).
- (2G) and (2.5G) were digital technologies such as GSM (global system for mobile communication). North America was a late adopter of this technology so several other competing standard also existed. The different 2G technologies either combined FDM and TDM (this is what GSM does) or used a technique called CDMA (code division multiple access). The latter uses different chipping sequences for each sender. GSM used 8Kbps compressed voice and had a data part of its standard called GPRS (general packet radio service). Speeds were up to 30-70Kbps or a little higher using EDGE (what iPhone 1 used (2007)).
- (3G) makes use of a variant of CDMA called wideband-CDMA (w-CDMA). It can communicate at speeds up to 1.92 Mbps (what iPhone 3G used (2008))