More Planning
CS156
Chris Pollett
Nov 16, 2022











CS156
Chris Pollett
Nov 16, 2022
`Action(Fly(p, f\r\o\m, t\o),`
`\quad P\r\e\cond: At(p, f\r\o\m) ^^ Pla\n\e(p) ^^ Airp\o\rt(f\r\o\m) ^^ Airp\o\r\t(t\o),`
`\quad E\f\f\e\c\t: neg At(p, f\r\o\m) ^^ At(p, t\o)\quad )`
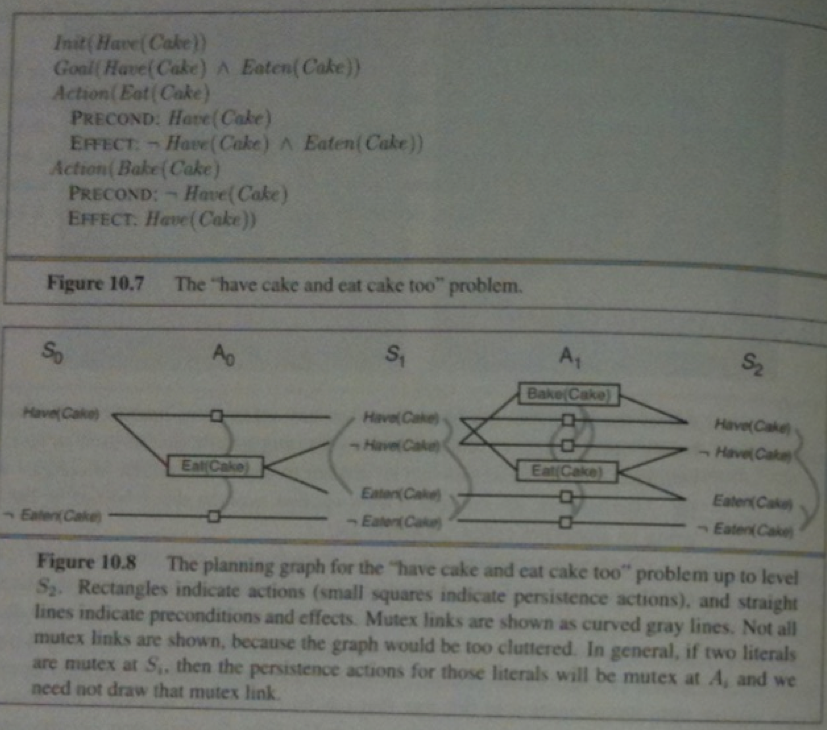
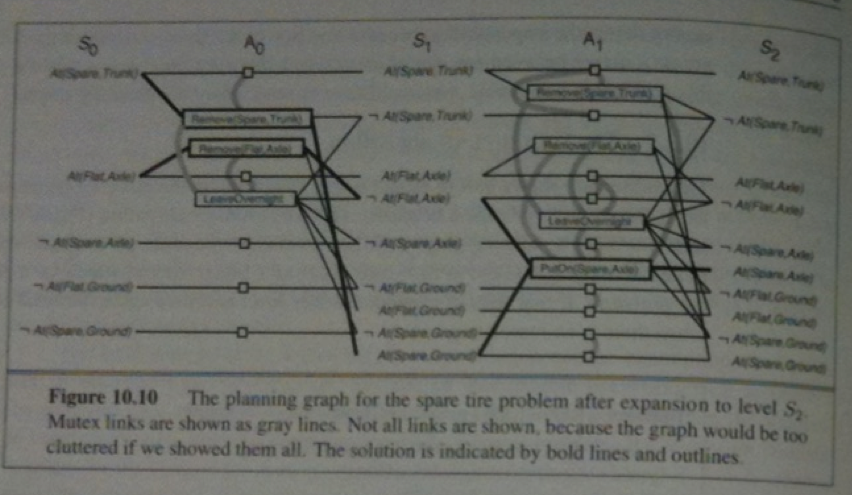
The GraphPlan algorithm is as follows:
function GraphPlan(problem) returns solution or failure:
graph := Initial-Planning-Graph(problem)
goals := Conjuncts(problem, Goal)
nogoods := empty hash table
for t= 0 to infty do:
if goals all present and non-mutex in S_t of graph then
solution := Extract-Solution(graph, goals, NumLevels(graph), nogoods)
if solution != failure then return solution
if graph and nogoods have not changed since t-1 then return failure
graph := Expand-Graph(graph, problem)
There are two common approaches to computing extract solution: