Minimax - Alpha-Beta Pruning
CS156
Chris Pollett
Sep 26, 2022











CS156
Chris Pollett
Sep 26, 2022
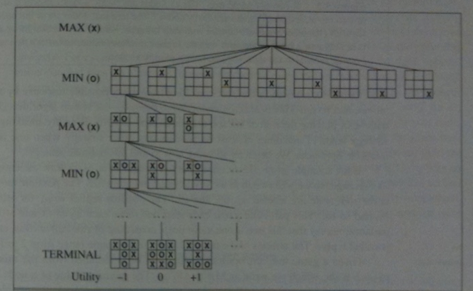
We consider games with two players MAX and MIN. A game consists of:
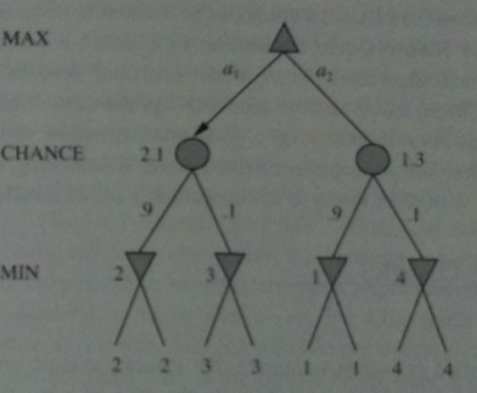
Which of the following is true?
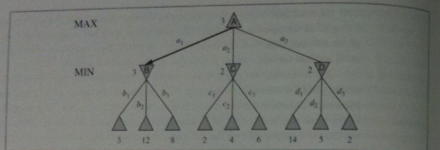
The minimax algorithm below computes the minimax decision from the current state. So we could use it to actually make an agent that could play a game.
Here `argmax_(a in s) f(a)` returns the element `a` of set `S` that has the maximum value of `f(a)`.
function MINIMAX-DECISION(state) return an action //it is assume is MAX's turn
return argmax_(a in ACTION(state)) MIN-VALUE(RESULT(state, a))
function MAX-VALUE(state) return a utility value
if (TERMINAL_TEST(state) == true) then return UTILITY(state, MAX)
v := -infty
for each a in ACTION(state) do
v := MAX(v, MIN-VALUE(RESULT(state, a)))
return v
function MIN-VALUE(state) return a utility value
if (TERMINAL_TEST(state) == true) then return UTILITY(state,MAX)
v := infty
for each a in ACTION(state) do
v := MIN(v, MAX-VALUE(RESULT(state, a)))
return v