










`A^\star`-Algorithm, Python
CS156
Chris Pollett
Aug 31, 2022











CS156
Chris Pollett
Aug 31, 2022
function A-STAR-SEARCH(problem) returns a solution, or failure
node := a node with STATE = problem.INITIAL-STATE, PATH-COST = 0,
H-COST = heuristic's cost to solution
frontier := a priority queue ordered by f=c+h, with node as
the only element
explored := an empty set
loop do
if EMPTY?(frontier) then return failure
node := POP(frontier) /* lowest f=c+h-value in frontier
since priority-queue */
if problem.GOAL-TEST(node.STATE) then return SOLUTION(node)
add node.STATE to explored
for each action in problem.ACTIONS(node.STATE) do
child := CHILD-NODE(problem, node, action)
if child.STATE is not in explored and child.STATE is not in frontier then
frontier := INSERT(child, frontier)
else if child.STATE is in frontier with higher f value
replace that frontier node with child
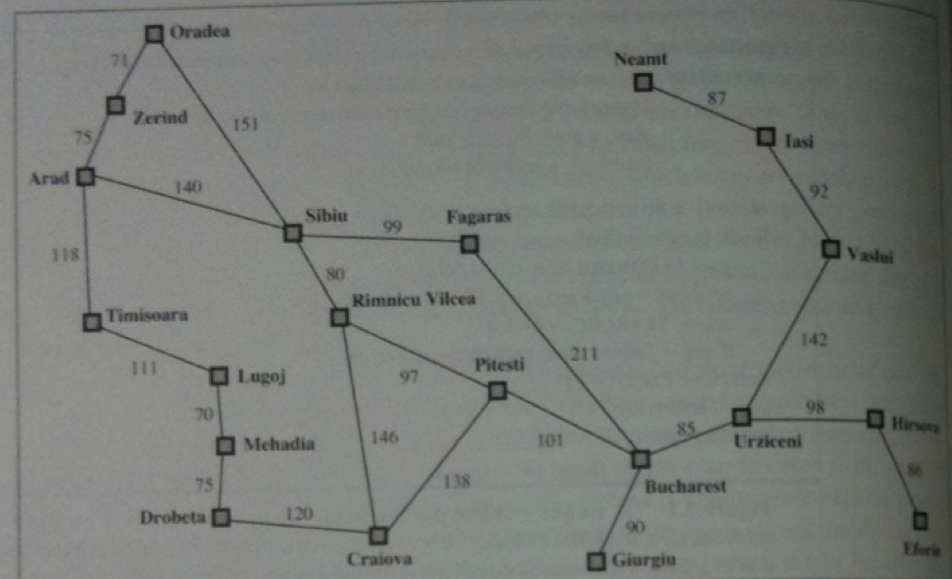
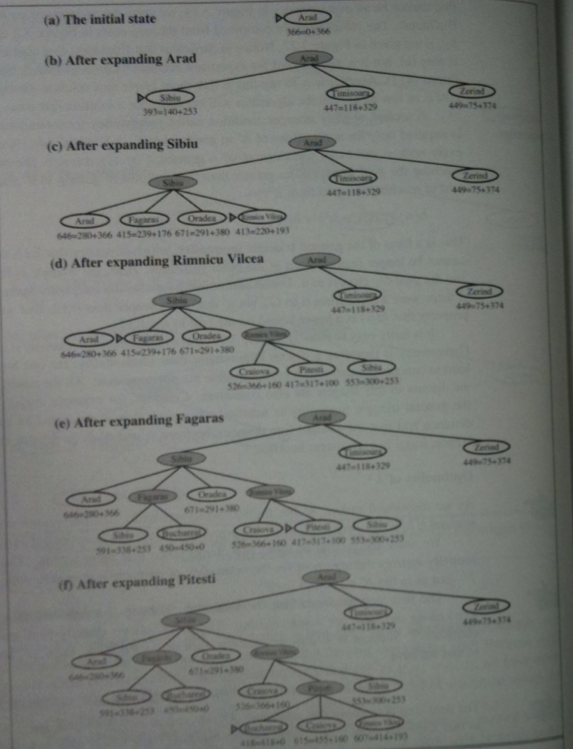
We will use the following road map of Romania to illustrate the `A^star`-algorithm:
| 6 | 2 | 8 |
| 1 | 4 | |
| 5 | 7 | 3 |
pythonat the command prompt. You should see something like:
Python 3.9.13 (main, May 24 2022, 21:28:31) [Clang 13.1.6 (clang-1316.0.21.2)] on darwin Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>>
>>>print("hello world")
which would print hello world to the terminal.