Adversarial Games
CS156
Chris Pollett
Feb 22, 2012











CS156
Chris Pollett
Feb 22, 2012
We consider games with two players MAX and MIN. A game consists of:
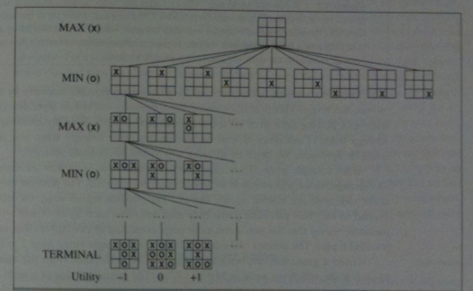
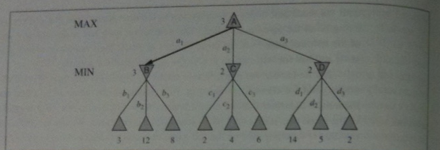
The minimax algorithm below computes the minimax decision from the current state. So we could use it to actually make an agent that could play a game.
Here `argmax_(a in s) f(a)` returns the element `a` of set `S` that has the maximum value of `f(a)`.
function MINIMAX-DECISION(state) return an action //it is assume is MAX's turn
return argmax_(a in ACTION(s)) MIN-VALUE(RESULT(state, a))
function MAX-VALUE(state) return a utility value
if (TERMINAL_TEST(state) == true) then return UTILITY(state)
v := -infty
for each a in ACTION(state) do
v := MAX(v, MIN-VALUE(RESULT(s, a)))
return v
function MIN-VALUE(state) return a utility value
if (TERMINAL_TEST(state) == true) then return UTILITY(state)
v := infty
for each a in ACTION(state) do
v := MIN(v, MAX-VALUE(RESULT(s, a)))
return v