Refactoring
Refactoring means improving the design of existing code.
Create a new project called flight.
Add two classes to flight: Aeroplane and Helicopter.
Add the following fields and methods to both classes:
double
speed;
double
altitude;
void
takeoff() {
speed
= 500;
altitude
= 10000;
}
void
land() {
speed
= 0;
altitude
= 0;
}
Extracting a Super Class
We can extract a super class and move selected methods and fields from subclasses to the superclass.
Select:
Refactor>Extract Superclass...
Here's the Extract Superclass dialog:
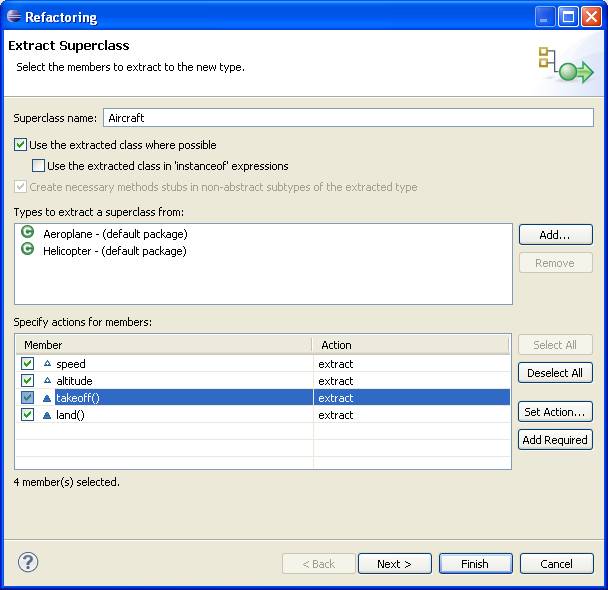
After this refactoring is performed, Aeroplane and Helicopter are empty subclasses of Aircraft, which contains their fields and methods.
Renaming a Class
We can rename a method, class, or field by selecting:
Refactor>Rename
Use this feature to rename "Aeroplane" "Airplane".
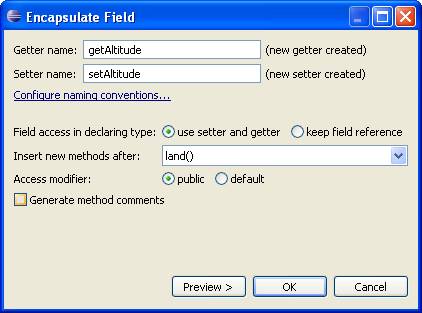
Encapsulate Fields
A quick way to add setters and getters to a selected field is to click:
Refactor>Encapsulate Fields...
Here's the dialog:
Here's the Aircraft code:
public class Aircraft {
private
double speed;
private
double altitude;
public
Aircraft() {
super();
}
void
takeoff() {
speed = 500;
setAltitude(10000);
}
void
land() {
speed
= 0;
setAltitude(0);
}
public
void setAltitude(double altitude) {
this.altitude
= altitude;
}
public
double getAltitude()
{
return
altitude;
}
public
void setSpeed(double speed) {
this.speed
= speed;
}
public
double getSpeed()
{
return
speed;
}
}
Pull Up/Push Down
Add the following code the Aircraft:
boolean canHover
= false;
void hover() {
if (canHover) {
setSpeed(0);
}
}
Add the following code to Airplane:
void speedUp() {
double amt = 50;
setSpeed(getSpeed() + amt);
}
void slowDown() {
double amt = 50;
setSpeed(getSpeed() - amt);
}
Use pull up and push down to relocate this code.
Converting Local Variables to Fields
Refactor the local variable amt found in speedUp and slowDown to fields.
Converting Fields to Local Variables
Extracting Constants
Use Extract Constant to get rid of the magic numbers in takeoff.