










Finish SVMs, Numpy
CS256
Chris Pollett
Sep 27, 2021











CS256
Chris Pollett
Sep 27, 2021
Suppose our training data is `X = {vec{x}_1, ..., vec{x}_k}`. Let `I = {1, ..., k}`. Let `X^+` be the positive examples, and `I^+` be the indices of the positive examples. Let `X^-` be the negative examples, and `I^-` be the indices of the negative examples. Define `X'`, `X^(+)'`, and `X^(-)'` as per the last slide.
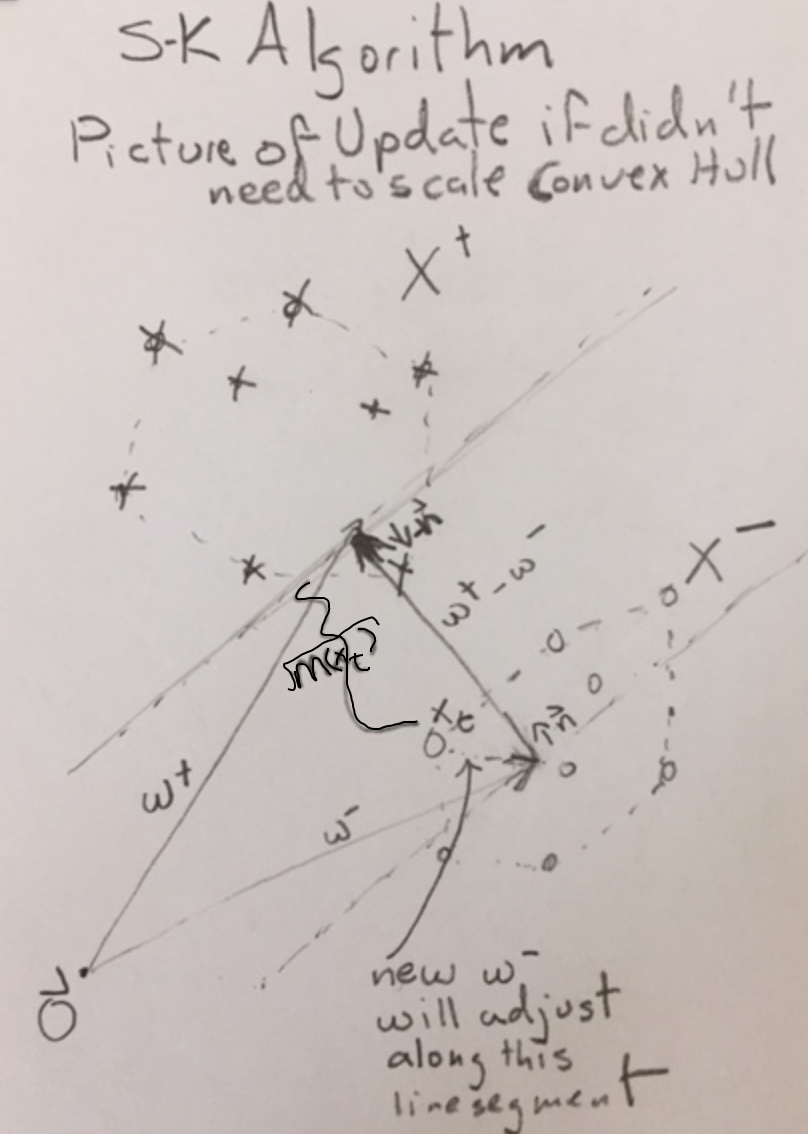
Which of the following is true?
import numpyor
import numpy as np
a = np.array([2, -1, 4, -8], float) type(a) #outputs <type 'numpy.ndarray'>
a = np.array((1,2,3), float)
a = np.array(range(1,5), float) # array([ 1., 2., 3., 4.])
a = np.arange(1,5, dtype=float) # this used a numpy method
#but also gives array([ 1., 2., 3., 4.])
a = np.arange(1,5,2, dtype=float) # array([ 1., 3.]) (used a stride of 2)
np.zeros(5, dtype=float) # array([ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]) np.ones((3,2), dtype=int) # array([[1, 1], [1, 1], [1, 1]]) # can give a shape np.identity(3, dtype=float) # 3x3 identity matrix np.random.rand(5) # an array of size 5 with random values between 0 and 1 np.random.rand(3, 4) # 3 x 4 array of random values between 0 and 1
b = a #copy by reference b[1] = 4 a # array([1, 4, 3]) c = a.copy() # a new array with the same entries as a c[1] = 5 a # array([1, 4, 3])
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], float) # a 2D array b = np.array([[[1,2], [2, 3]], [[4, 5], [6,7]]], float) # a 3d array
len(a) # 2 (the length of the first axis) a.shape # (2,3) a.reshape(6, 1) # array([[ 1.], [ 2.], [ 3.], [ 4.], [ 5.], [ 6.]]) c = b.flatten() # array([ 1., 2., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7.])
b = np.array([ 3., 4., 1., 5., 6., 2., 7.]) #notice type inference b.sort(); # now b is array([ 1., 2., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7.]) b.fill(4) # now b will contain array([ 4., 4., 4., 4., 4., 4., 4., 4.])
a[1][2] # outputs 6.0 on array a above b = np.array([2, -1, 4, -8], float) b[1] #outputs -1.0 b[2:] #outputs [4, -8.0]
b = np.array([2, -1, 4, -8], float) -8 in b #True for elt in b: print(elt)
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], float) b = a[1,:] #now b is array([ 4., 5., 6.]) c = a[:,2] # now c is array([ 3., 6.])
a = np.array([1, 2, 3, 5], int) a.sum() # 11 a.prod() #30 a.mean() # 2.75 np.median(a) # 2.5 a.var() # 2.1875 a.min() # 1 a.max() # 5 a.argmin() # 0 a.argmax() # 3
a = np.array([1, 2, 3], int) b = np.array([4, 5, 6], int) a + b # array([5, 7, 9]) a * b # array([ 4, 10, 18]) # notice point-wise multiplication (Hadamard product) b / a # array([4, 2, 2]) b % a # array([0, 1, 0]) b ** a # array([ 4, 25, 216]) a = np.array([[1, 2], [4, 5]], int) b = np.array([[5, 4], [1, 2]], int) a + b # array([[6, 6], [5, 7]]) a * b # array([[ 5, 8], [ 4, 10]]) # notice Hadamard product
a = np.array([1, 2, 3], float) np.exp(a) # array([ 2.71828183, 7.3890561 , 20.08553692])
a = np.array([1, 2, 3], int) b = np.array([4, 5, 3], int) z = a == b # array([False, False, True], dtype=bool) np.logical_not(z) # array([ True, True, False], dtype=bool) #numpy also support logical_and(z, w) and logical_or(z, w)
a.transpose()
a = np.array([1, -1, 1], float) b = np.array([3, -2, 4], float) np.dot(a, b) # 9.0 np.cross(a,b) # array([-2., -1., 1.])
a = np.array([[2,3],[4,5]], int) b = np.array([[0,3],[0,5]], int) np.dot(a,b) # array([[ 0, 21], [ 0, 37]])
a = np.array([[2,3],[4,5]], int) np.linalg.det(a) # -2.0 np.linalg.inv(a) #array([[-2.5, 1.5], [ 2. , -1. ]]) eivals, eivecs = np.linalg.eig(a) eivals # array([-0.27491722, 7.27491722]) eivecs # array([[-0.79681209, -0.49436913], [ 0.60422718, -0.86925207]])
np.roots([1,2,-3]) # array([-3., 1.])
#roots of polynomial x^2 + 2x - 3
np.poly([1,2,3,4]) # array([ 1, -10, 35, -50, 24])
#coeff's of poly with roots 1,2,3,4