










Reps and Data Structures for Reps
CS216
Chris Pollett
Mar 25, 2010











CS216
Chris Pollett
Mar 25, 2010
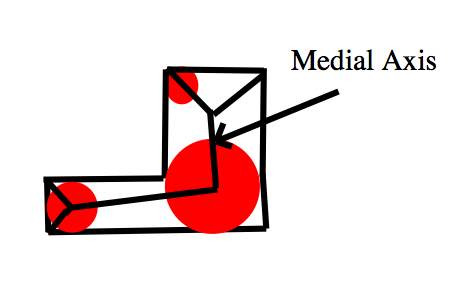
Definition. Let `X \subseteq \mathbb{R}^n`. A maximal disk in `X` is a closed disk `D^n(\vec{p}, r)` contained in `X` with the property that it is not properly contained in any other closed disk in `X`.
Definition. Let `X \subseteq \mathbb{R}^n`. The medial axis (MA) or skeleton or symmetric axis of `X` is the closure of the set of centers of maximal disks in `X`. The medial axis of a 3D solid is sometimes called a medial surface. The real-valued function that assigns to each center of a maximal disk in `X` the radius of that disk extends to a continuous function on the medial axis called the radius function.
Definition. A `d`-dimensional cell is said to be adjacent to an `e`-dimensional cell if:
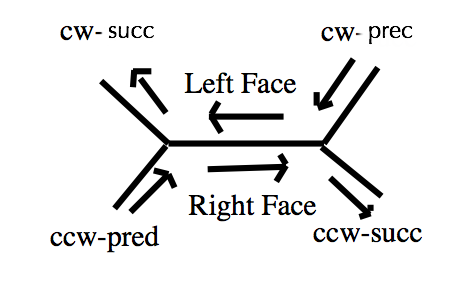
Here are some example data structures for Winged edge representation from Wikipedia:
class WE_Edge {
WE_Vertex vert1, vert2;
WE_Face aFace, bFace;
WE_Edge aPrev, aNext, bPrev, bNext; // clockwise ordering
WE_EdgeDataObject data;
}
class WE_Vertex {
List<WE_Edge> edges;
WE_VertexDataObject data;
}
class WE_Face {
List<WE_Edge> edges;
WE_FaceDataObject data;
}