










Local Storage, Tasks
CS185c
Chris Pollett
Mar 5, 2012











CS185c
Chris Pollett
Mar 5, 2012
<html>
<head>
<title>Local Storage Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
if (localStorage) {
document.write("<h1>Local Storage is Working!</h1>");
testStorage();
} else {
document.write("<h1>Local Storage is Unavailable!</h1>");
}
function testStorage()
{
myvalue = localStorage.getItem("mykey1");
myvalue2 = localStorage["mykey2"];
if(myvalue) {
document.write("<p>Found stored value for mykey1 ="+
myvalue+"</p>");
localStorage.removeItem("mykey1");
//can use localStorage.clear(); to get rid of everything
} else {
localStorage.setItem("mykey1", "hello");
}
if(myvalue2) {
document.write("<p>Found stored value for mykey2 ="+
myvalue2+"</p>");
} else {
localStorage["mykey2"] = "yo";
}
document.write("<h1>List all that's stored after update</h1>");
for (i=0; i<=localStorage.length-1; i++)
{
key = localStorage.key(i);
value = localStorage.getItem(key);
document.write("<p>("+key+", "+value+")</p>");
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
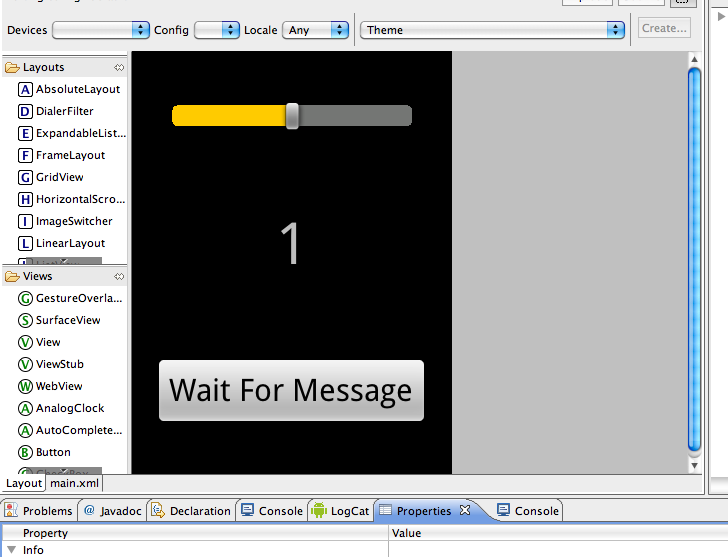
package org.pollett.TimerTest;
import org.pollett.TimerTest.R;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.AlertDialog;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.DialogInterface;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.SeekBar;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.SeekBar.OnSeekBarChangeListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.os.Handler;
public class TimerTest extends Activity {
Handler handler = new Handler(); //used to set up a delayed callback
SeekBar seekBar; //object associated with SeekBar on our Layour
TextView progressLabel; //object associated with our TextView label
AlertDialog alertDialog; //object used to hold our Alert
//Runnable object called after delay via Handler
Runnable alertTask = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
alertDialog.show();
}
};
/**
Called when the activity is first created.
Sets up all our the event listeners used in our example
*/
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
//set up the seekBar events to modify the label value
progressLabel = (TextView)this.findViewById(R.id.TextView01);
seekBar = (SeekBar)this.findViewById(R.id.SeekBar01);
seekBar.setOnSeekBarChangeListener(new OnSeekBarChangeListener() {
public void onProgressChanged(SeekBar seekBar, int progress,
boolean fromUser) {
progressLabel.setText(""+progress);
}
public void onStartTrackingTouch(SeekBar seekBar) {
//we're not doing anything here
}
public void onStopTrackingTouch(SeekBar seekBar) {
//we're not doing anything here
}
});
//set up our Alert Dialog but don't display it yet
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(this);
builder.setMessage("You've waited long enough!").setCancelable(true);
alertDialog = builder.create();
alertDialog.setButton("OK", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
return;
} });
// set up button, when button is clicked, use handler to schedule a task
Button waitButton = (Button)this.findViewById(R.id.Button01);
waitButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
handler.removeCallbacks(alertTask);
handler.postDelayed(alertTask, seekBar.getProgress()*1000);
}
});
}
}
Which of the following is true?
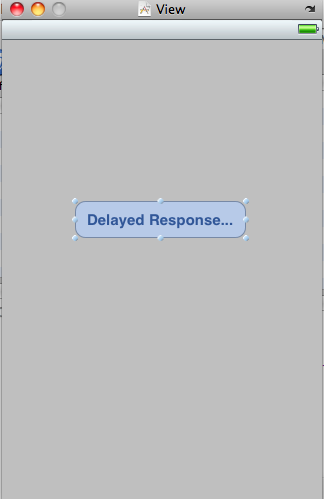
@interface NSTimerDemoViewController : UIViewController {
NSTimer *timer;
}
-(void) delayedResponse:(NSTimer*)theTimer;
-(IBAction) buttonPressed: (id) sender;
@end
-(IBAction) buttonPressed:(id) sender
{
timer = [NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval: 5.0 target:self
selector:@selector(delayedResponse:) userInfo:nil repeats:NO];
}
-(void) delayedResponse:(NSTimer*)theTimer {
UIAlertView *alert = [[UIAlertView alloc]
initWithTitle:@"Button Pressed -- Took A while"
message:@"You pressed the button, but I was napping"
delegate:nil
cancelButtonTitle:@"Yep, I did"
otherButtonTitles:nil];
[alert show];
[alert release];
}
After writing the above code, we connect the button up to buttonPressed in interface builder and the program should work.
setTimeout(myCallback, repeatTimeInMilliSec); // myCallback is the Javascript function you would like called
@class SwitchViewController; @interface AppDelegate : UIResponder <UIApplicationDelegate> @property (strong, nonatomic) UIWindow *window; @property (strong, nonatomic) SwitchViewController * switchViewController; @end
#import "AppDelegate.h" #import "SwitchViewController.h" @implementation AppDelegate @synthesize window = _window; @synthesize switchViewController; - (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions { self.window = [[UIWindow alloc] initWithFrame:[[UIScreen mainScreen] bounds]]; // Override point for customization after application launch. self.switchViewController = [[SwitchViewController alloc] initWithNibName:@"SwitchView" bundle:nil]; UIView *switchView = self.switchViewController.view; CGRect switchViewFrame = switchView.frame; switchViewFrame.origin.y += [UIApplication sharedApplication].statusBarFrame.size.height; switchView.frame = switchViewFrame; [self.window addSubview:switchView]; self.window.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor]; [self.window makeKeyAndVisible]; return YES; }
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h> @class BlueViewController; //similar to declaring something external in C @class YellowViewController; @interface SwitchViewController : UIViewController @property (strong, nonatomic) YellowViewController *yellowViewController; @property (strong, nonatomic) BlueViewController *blueViewController; -(IBAction) switchViews:(id) sender; @end