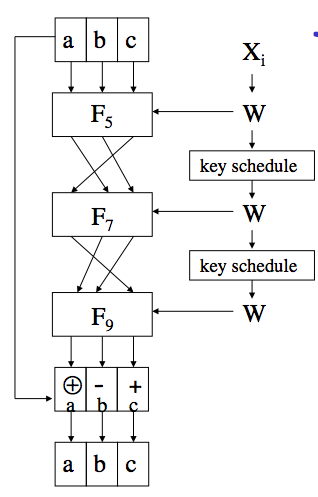
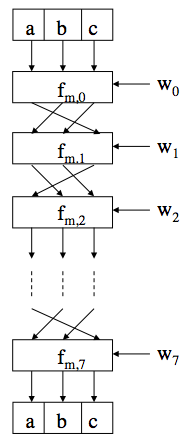
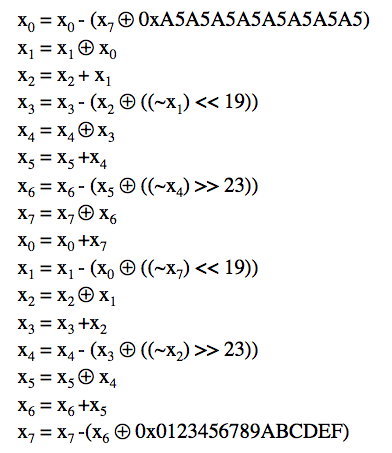Hash Functions
CS166
Chris Pollett
Oct 1, 2012











CS166
Chris Pollett
Oct 1, 2012
x32 + x26 + x23+ x22+ x16 + x12 + x11+ x10+ x8+ x7+ x5+ x4 + x2 + x1 +1
Problem 5.4 How many collisions would you expect to find in the following cases? (a) Your hash function generates a 12-bit output and you hash 1024 randomly selected messages. (b) Your hash function generates an `n`-bit output and you hash `m` randomly selected messages.
Answer: (a) The odds that a given message hash `h` is not shared with another message hash `h'` of the others is `1 - 1/2^(12)`. So the odds that 1023 other message hashes are different from `h` is `(1 - 1/2^(12))^(1023)`. So the expected number of message hashes that do not have other message hashes of the same value is `1024(1 - 1/2^(12))^(1023)`. So the expected number of message hashes that do have other message hashes of the same value is `1024(1 - (1 - 1/2^(12))^(1023)) approx 226`.
(b) Replacing 1024 with `m` in the previous derivation and `2^12` with `2^n`, give the equation `m(1 - (1 - 2^(-n))^(m-1))`.