Links and Encoding
CS158a
Chris Pollett
Feb. 9, 2011











CS158a
Chris Pollett
Feb. 9, 2011

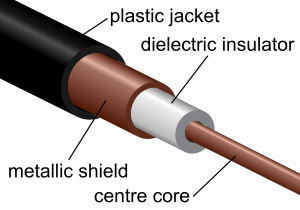
| Cable | Typical Bandwidths | Distance |
|---|---|---|
| Cat-5 Twisted Pair | 10-100Mbps | 100m |
| Thin-net Coax | 10-100Mbps | 200m |
| Thick-net Coax | 10-100Mbps | 500m |
| Multimode Fiber | 100Mbps | 2km |
| Single Mode Fiber | .1-10 Gbps | 40km |
| Service | Bandwidth |
|---|---|
| DS-1 | 1.544 Mbps |
| DS-3 | 44.736 Mbps |
| STS-1 | 51.840 Mbps |
| STS-3 | 155.250 Mbps |
| STS-12 | 622.080 Mbps |
| STS-24 | 1.244160 Gbps |
| STS-48 | 2.488320 Gbps |
| Service | Bandwidths |
|---|---|
| POTS | 28.8-56Kbps |
| ISDN | 64-128Kbps |
| xDSL | 128Kbps-100Mbps |
| CATV | 1-40Mbps |
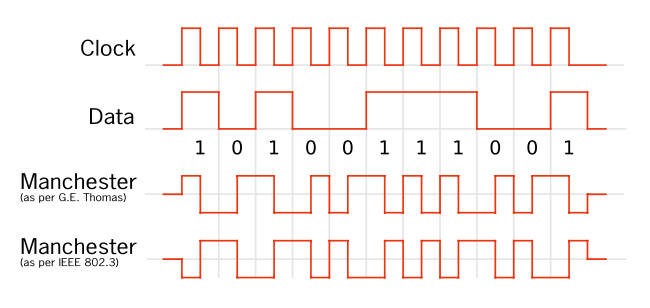
In the nonreturn to zero (NRZ) encoding we use high for a certain amount of time to represent a 1 and low for a certain amount of time to represent 0.
In the nonreturn to zero inverted (NRZI) encoding, to send a 1 the sender transitions from the current signal value to the opposite; to send a 0 the sender stays on the current signal.
In the Manchester encoding, one sends the XOR of the clock and the NRZ-encode data.