Local Search Algorithms
CS156
Chris Pollett
Sep 20, 2017











CS156
Chris Pollett
Sep 20, 2017
function SIMULATED-ANNEALING(problem, schedule) returns a solution state
inputs: problem, a problem
schedule, a mapping from time "temperature"
current := MAKE-NODE(problem.INITIAL_STATE)
for t = 1 to infty do
T := schedule(t) //typically as t gets larger schedule(t) is smaller
if(T == 0) return current //when Temperature is 0 return state
next := a randomly selected successor of current
DeltaE := next.value - current.value //estimated change in energy
if(DeltaE < 0) current := next
else current := next with probability e^(-DeltaE/T)
| 7 | 8 | 9 |
| 4 | 5 | 6 |
| @ 1 | 2 | 3 |
Suppose we wanted to do stochastic hill climbing on the above table of utilities. The agent starts in the square with the @ in it. The goal square would be a square of locally maximal utility. We want our choice of action to have probability proportional to its utilities, so that each possible action from a given square to an adjacent square has non-zero probability. Suggest an algorithm to do this. Then run your algorithm by hand and say what it does at each step until you get to the 9 in the upper right corner.
Post your solutions to the Sep 20 In-Class Exercise Thread.
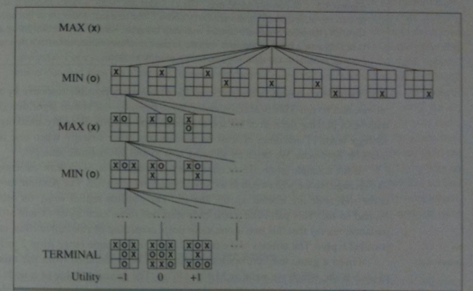
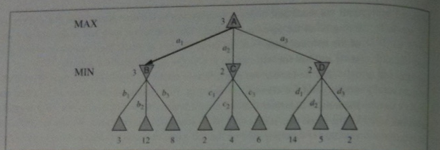
We consider games with two players MAX and MIN. A game consists of: