










`A^star`-algorithm, Python
CS156
Chris Pollett
Sep 8, 2014











CS156
Chris Pollett
Sep 8, 2014
function A-STAR-SEARCH(problem) returns a solution, or failure
node := a node with STATE = problem.INITIAL-STATE, PATH-COST = 0,
H-COST = heuristics cost to solution
frontier := a priority queue ordered by f=c+h, with node as
the only element
explored := an empty set
loop do
if EMPTY?(frontier) then return failure
node := POP(frontier) /* lowest f=c+h-value in frontier
since priority-queue */
if problem.GOAL-TEST(node.STATE) then return SOLUTION(node)
add node.STATE to explored
for each action in problem.ACTIONS(node.STATE) do
child := CHILD-NODE(problem, node, action)
if child.STATE is not in explored or frontier then
frontier := INSERT(child, frontier)
else if child.STATE is in frontier with higher f value
replace that frontier node with child
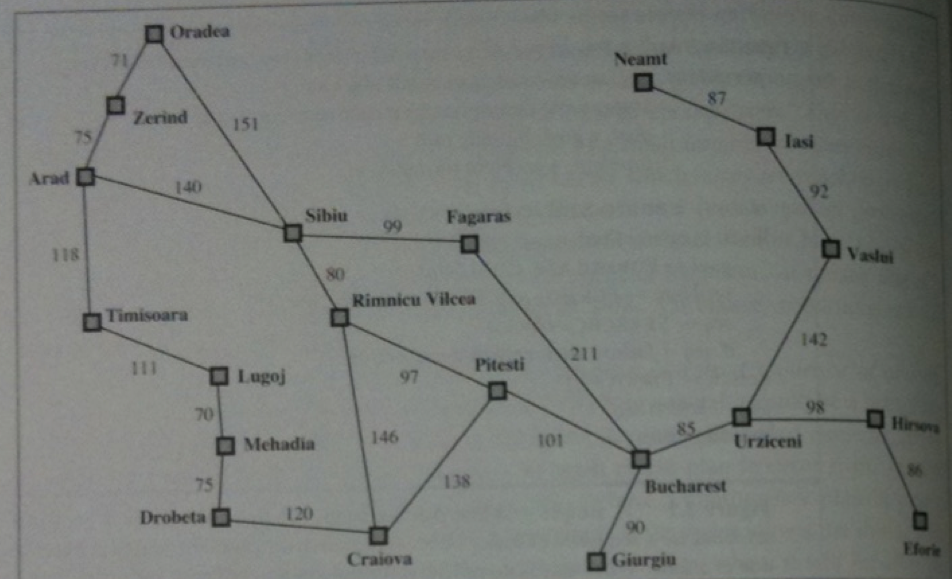
We will use the following road map of Romania to illustrate the `A^star`-algorithm:
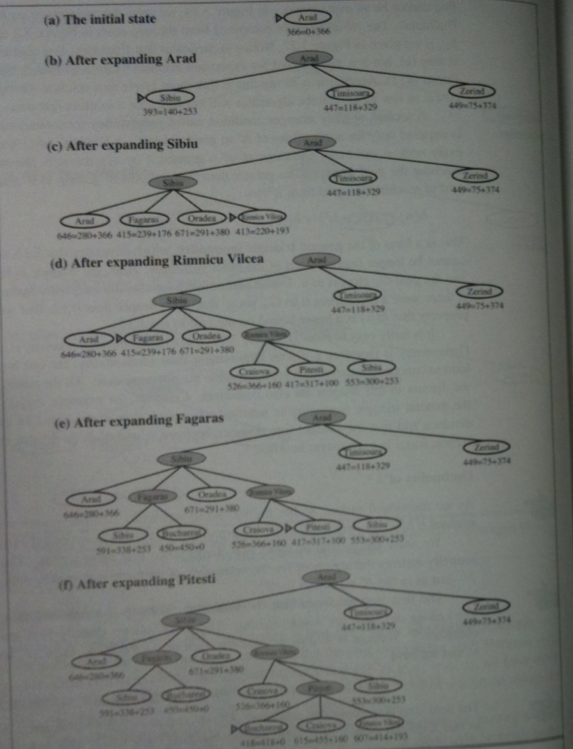
Which of the following is true?
pythonat the cmmand prompt. You should see something like:
Python 2.7.1 (r271:86832, Jun 16 2011, 16:59:05) [GCC 4.2.1 (Based on Apple Inc. build 5658) (LLVM build 2335.15.00)] on darwin Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>>
>>>print "hello world"which would print hello world to the terminal.
>>>2 / 3 + 7.9outputs 7.9; whereas, 2.0/3 + 7.9 outputs 8.566666666666666.
#!/usr/bin/env python # The above would mean don't have to type python when run under *nix # Comments begin with # print "Hello World"If we didn't have the first line or on Windows we would need to type "python hello.py" to run the program.
x = 7 x += 1 #note there are no ++ and -- operators x *= 3 y = 5 z = x - y print zwhich would print 19
print "%3d %0.2f" % (10, .9799)prints 10 with a leading space followed by 0.98
a = 5
if a > 4:
print "a is bigger than 4"
b = 99
if b < 50:
print "b is too little"
else:
print "b is big enough"
if a > 4 and b < 50:
print "1"
elif not a == 6:
print "2"
else:
print "3"
f = open("hello.py")
line = f.readline()
while line:
print line, #comma omits print's newline char
#print (line, end='') #in python 3
line = f.readline()
f.close()
for line in open("hello.py"):
print line,
to achieve the same affect
f = open("somefile.txt", "w")
print >>f, "%02f" %0.7999
f.write("hello")
f.close()
import sys
sys.stdout.write("Type something");
name = sys.stdin.readline()
a = "Hello" b = 'Good "bye"' c = """ Triple quotes one can go over multiple lines """ d = ''' this one works as well '''
a = "Hello World" b = a[4] # b is 'o' c = a[:5] # c is 'Hello' d = a[6:] # d is 'World' e = a[3:8] # e is "lo Wo"