










make, gdb - Back to Syntax
CS152
Chris Pollett
Sep 13, 2021











CS152
Chris Pollett
Sep 13, 2021
make targetThe make utility would then search the current directory for a file called Makefile and then tries to satisfy the target goal.
A Makefile consists of rules of the form:
target1: depends_on1 depends_on2 ... <tab>command1 <tab>command2 ... <blankline> target2: depends_on1 depends_on2 ... #etc # is used for a single-line comment
Notice the use of tabs is important!
myprog: myprog.o cc -o $@ $< myprog.o: myprog.c cc -c -o $@ $< # $@ refers to the target $< refers to the first dependency clean: rm -f myprog myprog.o
You can declare variables in a Makefile using the format varname = value like:
CC = gcc SUBDIRS = io linkedlist
These variables could then be used:
all : $(SUBDIRS) $(CC) historylesson.c -o historylesson
An example of a multi-line make rule might be something like:
io : @echo "Making io..." cd io make all
%.o : %.c
gcc -g myprog.c -o myprogwhere -g is the debugging flag.
gdb myprogThis would then give you the gdb prompt: (gdb)
Which of the following statements is true?
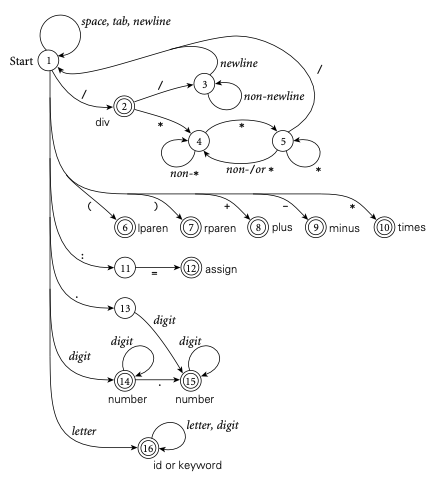
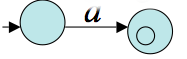
Assume now the result holds for regular expressions for which the total number of uses of union, `\star`, or concatenation is at most `n`. Consider `R` a regular language of complexity `n+1`. There are three cases to consider:
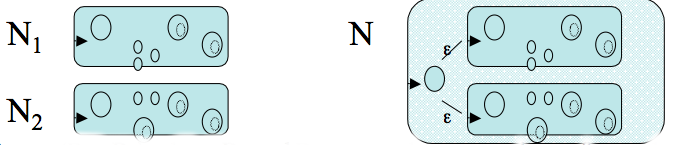
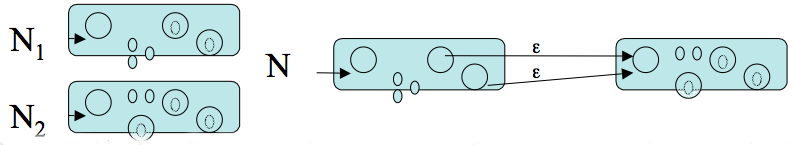
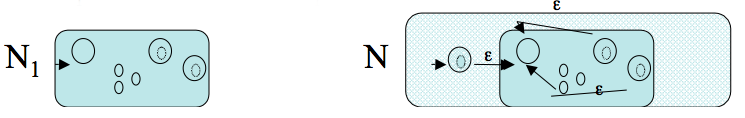
// compute bit vector reachable from B via epsilon transitions
BitVector E(BitVector B) {
BitVector oldB := new BitVector (B.length); //all zero bit vector of length n
BitVector eB = B;
while (eB != oldB) {
oldB = eB;
for (int i = 0; i < B.length; i++) {
BitVector tmpB = delta(i, epsilon); //states reachable from i by a single epsilon transition
eB = BitVector.or(eB, tmpB); //bitwise OR
}
}
return eB;
}
// here M =(Q, Sigma, delta, q_0, F)
boolean checkInNFA(String w, NFA M)
{
BitVector B = new BitVector(M.Q.length); // all 0 vector
B.setBit(0, 1); // indicate we could be in start state
int i = 0;
do {
B = E(B);
if (i == w.length) {
if (!BitVector.allZero(BitVector.and(B, M.F)) ) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// w[i] is ith symbol from w
BitVector tmpB = new BitVector(M.Q.length);
for (int j =0; j < M.Q.length; j++) {
if (B.isSet(i)) {
tmpB = BitVector.or(tmpB, M.delta(i, w[i]));
}
}
B = tmpB;
i++;
} while (i <= w.length);
return false; //shouldn't get here
}