The Persistence Layer
Not all objects can be saved to secondary memory (i.e., a file or a database). An object that can is called persistent. An object that cannot is called transient. Usually business objects representing customers, employees, transactions, etc. need to be persistent, while architectural objects such as UI components can be transient. By default, all Java objects are transient.
Saving objects to files is called serialization.
Most enterprise applications save persistent objects to relational databases.
See also:
Relational Databases
Here are some of the basic relational database concepts:
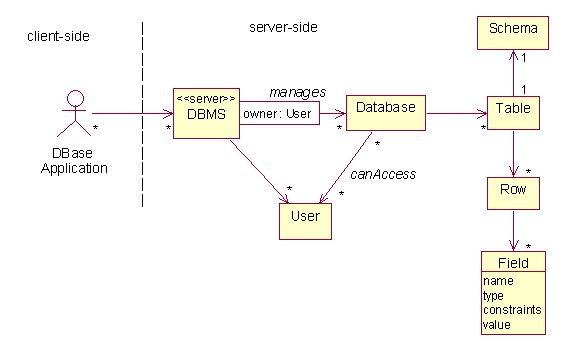
For example, a video rental store might have a database consisting of the following tables:
customer
employee
recording
rental
Here's a possible schema for the customer table:
customer(
customerID: INTEGER {pk},
LastName: VARCHAR(30),
FirstName: VARCHAR(20),
Phone: VARCHAR(10),
Suspended: BOOLE)
Here's a possible schema for the recording table:
recording(
recordingID: INTEGER {pk},
film: VARCHAR(30))
Here's a possible schema for the rental table:
rental(
rentalID: INTEGER {pk},
customerID: INTEGER {fk},
recordingID: INTEGER {fk},
checkedOut: DATE,
returned: DATE)
The Structured Query Language (SQL) is a standard language for manipulating data in a database. It provides basic commands for updating (update), deleting (delete), and inserting (insert) rows. It also provides a very powerful command called select for searching the entire database.
SELECT field1, field2, field3 ...
FROM table1, table2, table3 ...
WHERE condition
INSERT INTO table (field, field, ...)
VALUES (value, value, ...)
UPDATE table
SET field = value, ...
WHERE condition
DELETE FROM table WHERE condition
Semantic Gaps and Impedance Mismatch
The way data is represented in a relational database is similar to the way data is represented in an object-oriented program. We have the following analogies:
Object-Oriented Concept Relational
Database Concept
Class Table/Schema
Object Row
Field Field
Reference, OID Primary key
But there are additional OO concepts that don't have a relational equivalent: method, inheritance, polymorphism. We can think of this as a semantic gap between the object-oriented paradigm and the relational paradigm. This gap leads to the general problem of translating rows into objects and vice versa. A lot of programming effort goes into this problem. The term impedance mismatch is also used to refer to the difference in data representation between relational and object-oriented systems.
Gateways and Mappers
Gateways and Mappers are general patterns for hiding differences in data representation between two collaborating systems.
Table Gateway (DAO)
The idea of a table gateway is to provide a gateway class for each database table.
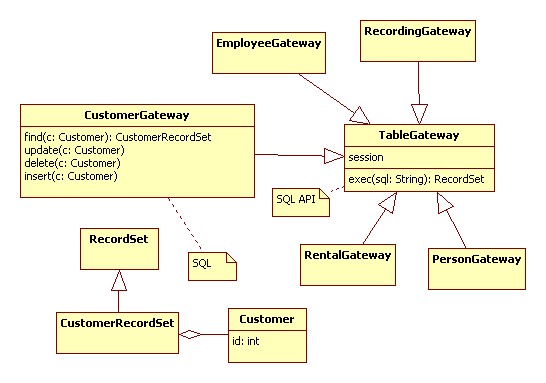
Here's a Java sketch of the find method in the CustomerGateway class:
class CustomerGateway extends Gateway {
CustomerRecordSet find(Customer c) {
CustomerRecordSet result = new
CustomerRecordSet();
String query = "select * from
customer where ";
if (c.ID != null) {
query += ("customerID =
" + c.getID());
} else {
// use c to add conditions to
query
}
ResultSet res = execute(sql);
// for each row in res add a
customer object to result
return result;
}
// etc.
}
A JDBC Gateway
public class Gateway {
protected String driver;
protected String dbms;
protected String dbase;
protected String dbaseName;
protected String user;
protected String password;
protected Connection connection;
protected Statement statement;
public Gateway(String driver,
String dbms,
String dbase,
String user,
String pswd) {
this.driver = driver;
this.dbms = dbms;
this.dbase = dbase;
this.user = user;
this.password = pswd;
this.dbaseName = dbms +
"/" + dbase;
try {
Class.forName(driver);
connection =
DriverManager.getConnection(
dbaseName,
user, password);
statement = connection.createStatement();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println(
"can't
connect to " + dbaseName + ": " + e);
try {
connection =
DriverManager.getConnection(
dbaseName + ";create=true");
statement =
connection.createStatement();
} catch (Exception e2) {
System.err.println(
"can't
create " + dbaseName + ": " + e2);
}
}
}
public void finalize() throws
SQLException {
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
public ResultSet execute(String sql)
throws SQLException {
ResultSet result = null;
if (statement.execute(sql)) {
result =
statement.getResultSet();
} else {
System.err.println("unrecognized
SQL: " + sql);
}
return result;
}
}