Client-Server Architectures
Clients send requests or queries to servers. Servers reply with
some sort of response:
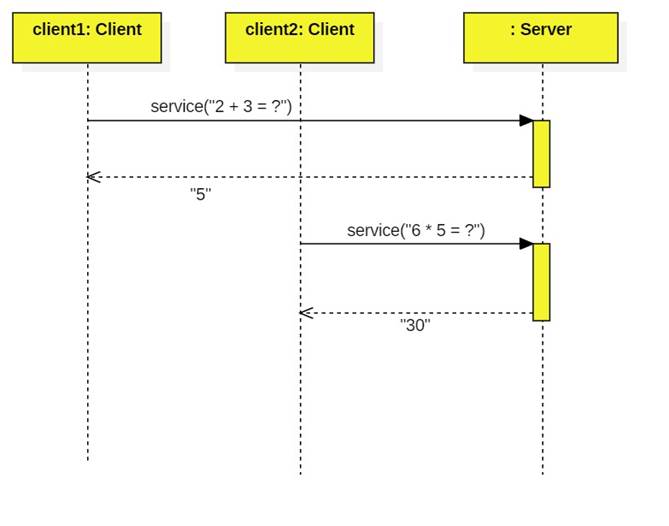
Examples of servers include web servers, database servers, and application servers.
Web and database browsers are examples of clients.
The types of requests and responses a server handles are
specified by a communication protocol. For example: HTTP, FTP, POP, SMTP,
TELNET, DNS, etc.
Protocols can be stateless or stateful.
In a stateless protocol such as HTTP, each request from a
client is considered to be independent of all previous requests from that
client. In other words, the server doesn't remember a client's previous requests.
Hacks such as cookies or embedding
strings in URLs need to be used to provide the server with these memories.
A stateful protocol allows client and server to have a back-and-forth
conversation:
