Systems Theory
Classifying Systems
Systems generally fall into one of the following categories:
Natural Systems
Examples from Biology include brains, people, redwood trees, and ecosystems.
Examples from Physics include solar systems, swinging pendulums, even the universe is a system.
Other examples from science include weather systems such as hurricanes, geological systems such as volcanoes and the earth's interior, and water systems such as ponds and creeks.
Social Systems
A social system consists of a population of goal-driven social agents. (A social agent interacts with other agents.) Examples of social systems include ant hills, bird flocks, bee hives, and angry mobs.
An economic system is a social system in which agents are businesses.
Engineered Systems
An engineered system is a man-made system that has a specific purpose. Examples include machines, bridges, dams, and computer programs.
Organizational Systems
An organization is an engineered social system. Examples include corporations, armies, governments, and clubs.
Definition
Formally, a system, S, consists of the following sets and functions:
1. Inputs = a set of possible inputs
2. Outputs = a set of possible outputs
3. States = a set of possible internal states
4. update = a function of the form:
update(input, currentState) = (output, newState)
5. controlLoop = a mechanism that executes the algorithm:
1. currentState =
initialState
2. read input
3. (output, newState) = update(input,
currentState)
4. currentState = newState
5. write output
6. if currentState is not terminal,
then goto 2.
Example
A market is a system. The inputs are the supply and demand for a given product, the state is the price of the product. The update function determines how changes in supply and demand affect price.
Example
A running word processor is a system.
Example
A computer executing a program is a system. The inputs are character strings entered at the keyboard, the outputs are character strings displayed on the monitor, the current state is the entire content of memory at a given moment in time, including the instruction pointer. The update function tells how memory changes and what output is produced when the instruction referenced by the instruction pointer is executed. The control loop is the fetch-execute cycle executed by the CPU.
Example
A computer chip or integrated circuit (IC) is a system. The set of input ICs can be classified as sequential or combinatorial.
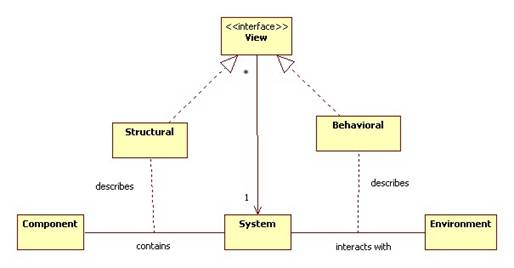
System Views
A system can be viewed or modeled from different perspectives. The most important views are the external, behavioral, or functional view and the internal or structural view.
The External View of a System
The external view models the system in terms of its interaction with the external environment. This is also called the functional view because it models the system as a function that transforms inputs (stimuli) into outputs (responses).
Example: Classical Behavioral Psychology modeled people and other animals as stimulus-response machines. For example, given the stimulus of a ringing bell, Pavlov's dogs reliable produces the response of salivation.
Example: Computer chips can be classified as An computer chip (integrated circuit) is a system. The external view specifies how
The Internal View of a System
Internally, a system can be viewed as a network of interacting components.
Example:
Internally, a computer is a collection of computer chips interconnected through the system bus or motherboard.