The Java
Collections Framework (JCF)
JCF defines four basic interfaces and numerous implementations of these interfaces:
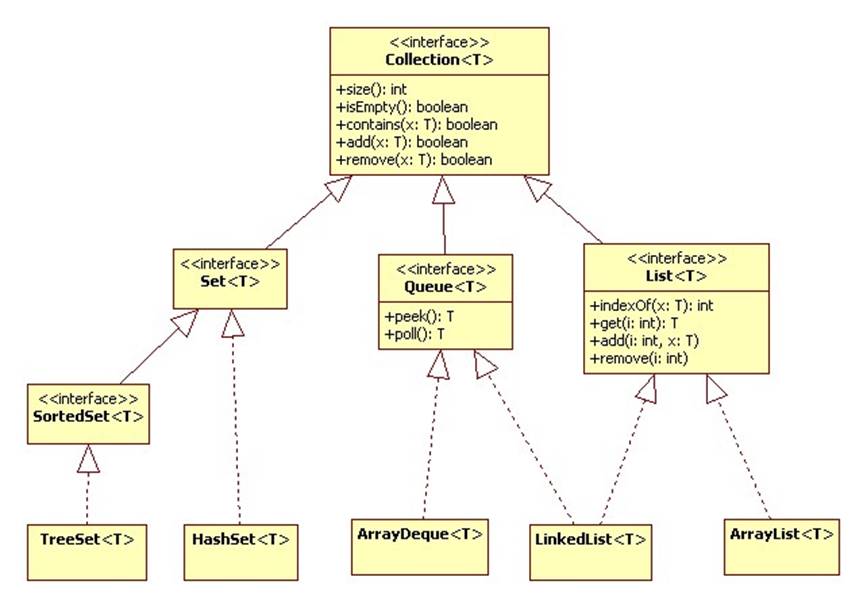
All of these classes and interfaces are contained in the java.util package.
Notice that all interfaces and implementations are parameterized by the type of objects they contain.
For example:
Collection<Integer> scores = new TreeSet<Integer>();
SortedSet<Date> appointments = new TreeSet<Date>();
Set<Employee> staff = new HashSet<Employee>();
List<City> itinerary = new ArrayList<City>();
Queue<Event> schedule = new LinkedList<Event>();
Collections
Collection<T> defines the basic interface that allows users to add and remove elements of type T:
public interface Collection<T> {
// Basic Operations
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
boolean contains(T element);
boolean add(T element); // Optional
boolean remove(T element); // Optional
Iterator<T> iterator();
// Bulk Operations
boolean containsAll(Collection<T>
c);
boolean addAll(Collectio<T>n c); // Optional
boolean removeAll(Collection<T>
c); // Optional
boolean retainAll(Collection<T>
c); // Optional
void clear(); // Optional
// Array Operations
T[] toArray();
T[] toArray(Object a[]);
// Overrides
boolean equals(Object o);
int hashCode();
}
Note that Java does not provide an implementation of this interface. Instead, Java provides implementations of more specific interfaces. A direct implementation of Collection would be a multiset.