Calcutron (An desktop utility)
Overview
Calcutron is a calculator utility similar to the calculator that comes with MS Windows:
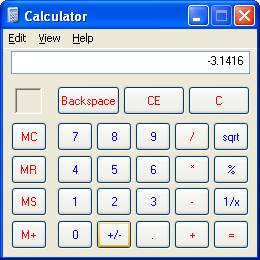
Calcutron allows users to perform arithmetic on floating point numbers that can have as may as 32 digits. Users can store an intermediate result in a memory cell. The stored result can be erased or recalled.
Requirements Model
Functional Requirements (Use Cases)
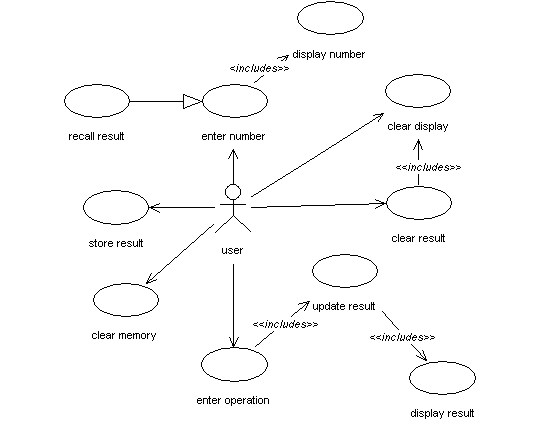
Use Case Elaborations
Enter Number/Display Number
The user enters a number one digit at a time and the number is displayed. The number may contain up to 32 digits, a decimal point, and a minus sign.
Main Scenario
Here is how the user would enter -12.32:
user: enters 1
system: display = 10 * 0 + 1 = 1
system: displays 1
user: enters 2
system: display = 10 * 1 + 2 = 12
system: displays 12
user: enters .
system: decimal mode on
user: enters 3
system: display = 10 * 12 + 3 = 123
system: display = display/10 = 12.3
system: displays 12.3
user: enters 2
system: display = 100 * display + digit = 1232
system: display = display/100 = 12.32
system: displays display
user: enters -
system: display = -1 * display
Alternate Scenarios
User enters 0, -, or . at an inappropriate time.
User enters too many digits.
Enter Operation
The user can enter any of the following operations:
+, -, /, *
Entering an operation combines the current result with the display using the previously entered operation, then overwrites this operation with the entered operation.
Main Scenario
user: enters operation
system: result = result combined with display using last operation
system: displays result
system: clears display
system: last operation = entered operation
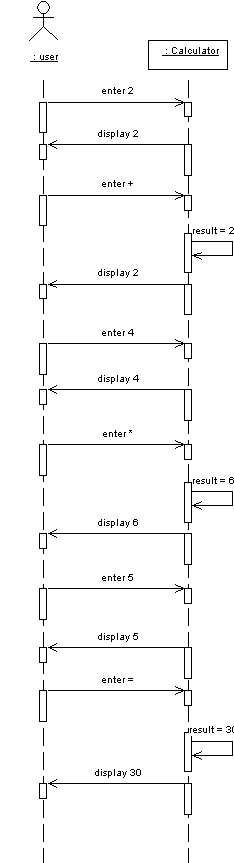
For example, here is how the user computes 2 + 4 * 5
user: enters 2
system: display = 2
user: enters +
system: result = 2
system: nextOp = +
system: displays 2
user: enters 4
system: display = 4
user: enters *
system: result = 4 + 2 = 6
system: nextOp = *
system: displays 6
user: enters 5
system: displays 5
user: enters =
system: result = 6 * 5 = 30
system: nextOp = ?
system: displays 30
We can display this same information using a sequence diagram:
Alternate Scenarios
User enters operator at an inappropriate time
User attempts to divide by 0
Overflow
Underflow
Clear Display/Clear Result
Main Scenarios
user: enters clear display (CE)
system: display = 0
system: displays 0
user: enters clear result (C)
system: result = 0
system: clears display
Store Result/Recall Result/Clear Memory
The user may store the displayed number in memory and recall it later.
Main Scenario
user: enters number
system: computes and displays number
user: stores number (M)
system: memory = number
user:
Non-Functional Requirements
Usability
Reliability
Performance
Supportability
Domain Model
Design Model
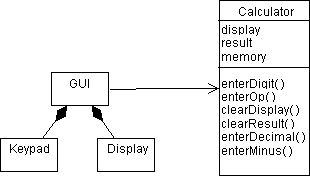
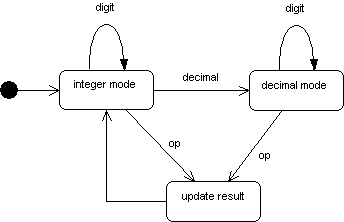
Implementation Model
public class Calculator {
private double result = 0, display = 0,
memory = 0, shift = 10;
private boolean decimalMode = false;
char nextOp = '?';
public void enterDigit(int digit) {
display = shift * display + digit;
if (decimalMode) {
display = display/shift;
shift = 10 * shift;
}
System.out.println("display =
" + display);
}
public void enterDecimal() {
decimalMode = true; }
public void enterNegative() { display =
-1 * display; }
private void updateResult() {
System.out.println("operator =
" + nextOp);
switch(nextOp) {
case '+': result += display;
break;
case '*': result *= display;
break;
case '-': result -= display;
break;
case '/': result /= display;
break;
default: result = display;
}
display = 0;
shift = 10;
decimalMode = false;
System.out.println("result =
" + result);
}
public void enterOp(char theOp) {
updateResult();
nextOp = theOp;
}
public void clearDisplay() {
display = 0;
shift = 10;
decimalMode = false;
System.out.println("display =
" + display);
}
public void clearResult() {
result
= 0;
nextOp = '?';
clearDisplay();
}
}