When a problem occurs, Java attempts to transfer control to a method that can deal with the problem. Such methods are called exception handlers. An exception handler can either correct the problem (fault handlers), gracefully terminate the program (trap handlers), or simply ignore the problem.
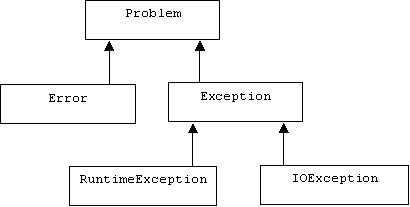
Java recognizes two types of problems: errors and exceptions. Exceptions can be further divided into I/O exceptions and runtime exceptions:

Errors are system errors, such as memory exhaustion. Programmers should not attempt to handle these. Runtime exceptions are programming errors, such as a bad cast, an out-of-bounds array access, or a null pointer access. I/O exceptions occur when bad things happen to an otherwise good program, such as trying to open a file that doesn't exist.
As in C++, the syntax for throwing an exception is:
If a method explicitly or implicitly throws an exception, it must explicitly declare so in its header:
The following program computes and displays sqrt3(x) for x = 16 and x = -16. In the second case, the attempt to compute sqrt(-16) throws a custom "negative number" exception, which is handled by the caller of the caller. We begin by declaring an exception class. This step isn't necessary if you're happy with existing exception classes:
class NegativeNumberException
extends IOException
{
public NegativeNumberException(double
irritant)
{
super("non-negative number expected, not " + irritant);
}
public NegativeNumberException()
{
super("non-negative number expected");
}
}
class ExceptionDemo
{
public static double
squareRoot(double x) throws NegativeNumberException
{
System.out.println("Entering squareRoot()");
if (x < 0)
{
NegativeNumberException exp
= new NegativeNumberException(x);
throw(exp);
}
System.out.println("Exiting squareRoot()");
return Math.sqrt(x);
}
public static double
cubeOfSquareRoot(double x) throws NegativeNumberException
{
System.out.println("Entering cubeOfSquareRoot()");
double temp = squareRoot(x); // may implicitly throw exception here
System.out.println("Exiting cubeOfSquareRoot()");
return temp * temp * temp;
}
public static void
displayCubeOfSquareRoot(double x)
{
double result = 0;
System.out.println("Entering displayCubeOfSquareRoot()");
try
{
result = cubeOfSquareRoot(x);
}
catch(NegativeNumberException e)
{
System.err.println("Error: " + e);
// more steps here?
}
System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.println("Exiting displayCubeOfSquareRoot()");
}
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Entering main()");
System.out.println("calling displayCubeOfSquareRoot(16)");
displayCubeOfSquareRoot(16);
System.out.println("calling displayCubeOfSquareRoot(-16)");
displayCubeOfSquareRoot(-16); // trouble
System.out.println("Exiting main()");
}
} // ExceptionDemo