Graphical User Interfaces
Concepts
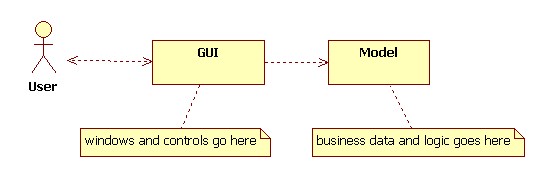
Controls
A control is something the user can manipulate in order to send commands to an application. Buttons, text fields, labels, menus, and scroll bars are examples of controls.
Many controls are contained in javax.swing:
JButton
JLabel
JTextField
Panels
A (control) panel is a component that holds controls and sub-panels.
javax.swing.JPanel
A panel is a window that has no border.
We can think of a GUI as a tree. Panels are parent nodes in this tree. Controls are the leaves.
Listeners
A listener is an object that registers with one or more controls. Each time a control is activated by a user, it calls a special method inside every registered listener.
javax.awt
interface ActionListener {
void actionPerformed(ActionEvent ae);
}
Structure
Here's the basic structure of most applications:
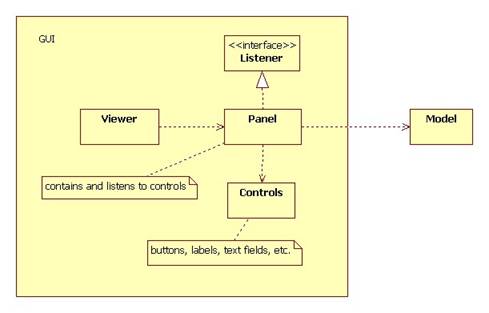
Here is a Java sketch of a panel:
class ControlPanel extends JPanel implements ActionListener {
private JButton aButton; // etc.
private Model myModel;
public ControlPanel(Model m) {
myModel = m;
aButton = new
JButton("OK");
add(aButton); // add a child button
to this panel
aButton.addActionListener(this); //
this = the control panel
// etc.
}
public void paintComponent(Graphics gc)
{
super.paintComponent(gc); // paint
children
Graphics2D gc2d = (Graphics2D)gc;
myModel.draw(gc2d); // draw a
picture of my model
// any additional background
graphics can go here
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent
ae) {
if
(ae.getActionCommand().equals("OK")) {
// OK button clicked, do
something to the model
}
repaint(); // call paintComponent()
}
}
Example 1
Output
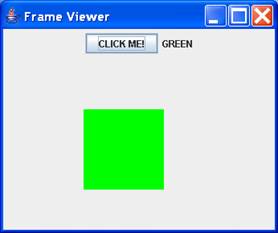
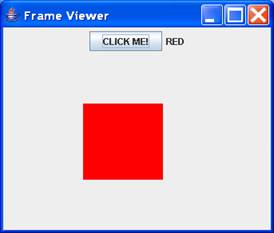
Imports
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
Viewer
public class PanelViewer {
public static final int FRAME_WIDTH =
300;
public static final int FRAME_HEIGHT =
400;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
JFrame frame = new JFrame();
frame.setSize(FRAME_WIDTH,
FRAME_HEIGHT);
frame.setTitle("Frame
Viewer");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
ControlPanel panel = new ControlPanel();
// CalculatorPanel panel = new CalculatorPanel();
frame.add(panel);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Panel
class ControlPanel extends
JPanel implements ActionListener {
private
JButton button;
private JLabel label;
private
Color myModel;
public ControlPanel() {
button
= new JButton("CLICK ME!");
add(button);
button.addActionListener(this);
label = new JLabel("RED");
add(label);
myModel = Color.RED;
}
public void paintComponent(Graphics gc)
{
super.paintComponent(gc);
// paint children
gc.setColor(myModel);
gc.fillRect(100, 100, 100, 100);
}
public
void actionPerformed(ActionEvent ae) {
if (color.equals(Color.RED)) {
myModel = Color.GREEN;
label.setText("GREEN");
} else {
myModel = Color.RED;
label.setText("RED");
}
repaint();
}
}
Example 2
Output
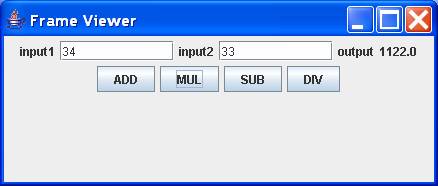
Panel
class CalculatorPanel extends JPanel implements ActionListener {
private
JTextField input1, input2;
private JLabel output;
private JButton addButton, mulButton,
subButton, divButton;
public CalculatorPanel() {
input1 = new JTextField(10);
JLabel label = new
JLabel("input1");
add(label);
add(input1);
input2 = new JTextField(10);
label = new JLabel("input2");
add(label);
add(input2);
output = new JLabel("0");
label = new
JLabel("output");
add(label);
add(output);
addButton = new
JButton("ADD");
add(addButton);
addButton.addActionListener(this);
mulButton = new
JButton("MUL");
add(mulButton);
mulButton.addActionListener(this);
subButton = new
JButton("SUB");
add(subButton);
subButton.addActionListener(this);
divButton = new
JButton("DIV");
add(divButton);
divButton.addActionListener(this);
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent
ae) {
double arg1 = new
Double(input1.getText());
double arg2 = new
Double(input2.getText());
String cmmd = ae.getActionCommand();
if (cmmd.equals("ADD")) {
output.setText("" +
(arg1 + arg2));
} else if(cmmd.equals("MUL"))
{
output.setText("" +
(arg1 * arg2));
} else if(cmmd.equals("SUB"))
{
output.setText("" +
(arg1 - arg2));
} else if(cmmd.equals("DIV"))
{
output.setText("" +
(arg1 / arg2));
} else {
output.setText("0");
}
}
}
Example 2.1
Note: This GUI has no model. We could have created a calculator class:
class Calculator {
public void add(double arg1, double
arg2) {
return arg1 + arg2;
}
public void mul(double arg1, double
arg2) {
return arg1 * arg2;
}
public void sub(double arg1, double
arg2) {
return arg1 - arg2;
}
public void div(double arg1, double
arg2) {
return arg1 / arg2;
}
}
Here is the new CalculatorPanel class:
class CalculatorPanel extends JPanel implements ActionListener {
private
JTextField input1, input2;
private JLabel output;
private JButton addButton, mulButton,
subButton, divButton;
private Calculator myModel;
public CalculatorPanel() {
myModel = new Calculator();
// etc.
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent
ae) {
double arg1 = new
Double(input1.getText());
double arg2 = new
Double(input2.getText());
String cmmd = ae.getActionCommand();
if (cmmd.equals("ADD")) {
output.setText("" + myModel.add(arg1,
arg2));
} else if(cmmd.equals("MUL"))
{
output.setText("" + myModel.mul(arg1,
arg2));
} else if(cmmd.equals("SUB"))
{
output.setText("" + myModel.sub(arg1,
arg2));
} else if(cmmd.equals("DIV"))
{
output.setText("" + myModel.div(arg1,
arg2));
} else {
output.setText("0");
}
}
}