Arrays
Declaring & Initializing Arrays
An array is a named sequence of contiguous variables of the same type.
The following declarations declare two length 0 arrays:
double[] scores;
Point[] locations;
Assume the following declaration:
int CAP = 10;
We can initialize these to length 10 arrays as follows:
scores = new double[CAP];
locations = new Point[CAP];
Of course the declaration and initialization can be a single line:
double[] scores = new double[CAP];
Point[] locations = new Point[CAP];
Each variable in an array can be accessed using subscript notation. For example, here is how we can increment each score:
for(int index = 0; index < scores.length; index++) {
scores[index] = scores[index] + 1;
}
Note that scores.length = 10.
Note that the index ranges from 0 to 9. This can be a source of errors. For example:
scores[10] = scores[10] + 1; // ERROR!
Will cause an "index out of range" error.
Note: At this point locations[index] == null for each index, while scores[index] = 1.0.
If the elements are known in advance, a small array can be initialized as follows:
int[] primes = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11};
We can also create anonymous arrays to be passed as inputs to methods:
computeAverage(new double[] {43.5, 62.7, 83.1});
Array Processing
Example: Vector Arithmetic
class VectorUtils {
public static double[] add(double[]
vec1, double[] vec2) {
if (vec1.length != vec2.length) {
System.err.println("Vectors
must have same dimension");
System.exit(1);
}
int dim = vec1.length;
double[] result = new double[dim];
for(int i = 0; i < dim; i++) {
result[i] = vec1[i] + vec2[i];
}
return result;
}
public static void display(double[]
vec) {
System.out.print("<");
for(int i = 0; i < vec.length;
i++) {
System.out.print(" " +
vec[i]);
}
System.out.println("
>");
}
public static double dot(double[] vec1,
double[] vec2) {
if (vec1.length != vec2.length) {
System.err.println("Vectors
must have same dimension");
System.exit(1);
}
int dim = vec1.length;
double result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < dim; i++) {
result += vec1[i] * vec2[i];
}
return result;
}
public static double length(double[]
vec) {
return Math.sqrt(dot(vec, vec));
}
}
public class VectorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] v1 = {3, 4, 5};
double[]
v2 = {2, 1, -7};
double[] v3 = VectorUtils.add(v1,
v2);
System.out.print("sum =
");
VectorUtils.display(v3);
System.out.println("dot =
" + VectorUtils.dot(v1, v2));
System.out.println("Length of
v3 = " + VectorUtils.length(v3));
}
}
Program Output
sum = < 5.0 5.0 -2.0 >
dot = -25.0
Length of v3 = 7.3484692283495345
Example: Statistics
class StatUtils {
/** = avg */
public static double mean(double[]
data) {
double result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < data.length;
i++) {
result += data[i];
}
return result/data.length;
}
public static double max(double[] data)
{
double result =
Double.NEGATIVE_INFINITY;
for(int i = 0; i < data.length;
i++) {
result = Math.max(result,
data[i]);
}
return result;
}
/** = mean distance from mean */
public static double
standardDeviation(double[] data) {
double mean = mean(data);
double result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < data.length;
i++) {
result += (data[i] - mean) *
(data[i] - mean);
}
result = result/(data.length - 1);
result
= Math.sqrt(result);
return result;
}
}
public class TestStatUtils {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] scores = new double[10];
scores[0] = 87;
scores[1] = 93;
scores[2] = 64;
scores[3] = 59;
scores[4] = 70;
scores[5] = 72;
scores[6] = 75;
scores[7] = 25;
scores[8] = 80;
scores[9] = 71;
System.out.println("mean =
" + StatUtils.mean(scores));
System.out.println("max =
" + StatUtils.max(scores));
System.out.println("sd = "
+
StatUtils.standardDeviation(scores));
}
}
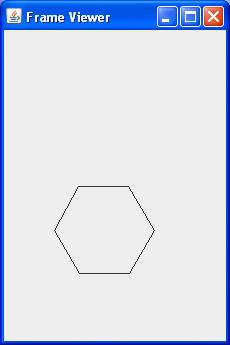
Example: Polylines
Imports
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import javax.swing.*;
Viewer
public class PolyViewer {
public static final int FRAME_WIDTH =
300;
public static final int FRAME_HEIGHT =
400;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
JFrame frame = new JFrame();
frame.setSize(FRAME_WIDTH,
FRAME_HEIGHT);
frame.setTitle("Frame
Viewer");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// create custom component:
PolyComponent component = new
PolyComponent(6, 50, 100, 200);
frame.add(component);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Component
class PolyComponent extends JComponent {
private Polygon poly;
public PolyComponent(int numVerts, int
radius, int xc, int yc) {
int[] x = new int[numVerts];
int[] y = new int[numVerts];
double angle = 2 * Math.PI/numVerts;
for(int i = 0; i < numVerts; i++)
{
x[i] = (int)(xc + radius *
Math.cos(i * angle));
y[i] = (int)(yc + radius *
Math.sin(i * angle));
}
poly = new Polygon(x, y, numVerts);
}
public void paintComponent(Graphics gc)
{
Graphics2D gc2d = (Graphics2D)gc;
gc2d.draw(poly);
}
}
Output
Collections
A collection is any class that manages an array of member values. The public interface would usually include the following methods:
class Collection {
/** = index of possibleMember or -1 */
public int find(Member possibleMember)
{ ... }
/** = Member at index or error */
public Member get(int index) { ... }
/** = # of members */
public int getSize() { ... }
/** adds a new member if not already a
member */
public void add(Member newMember) { ...
}
/** removes existing member */
public void remove(Member oldMember) {
... }
}
Where Member is any class or type.
Example: Organizations
class Organization {
private int cap;
private int size;
private static final int SEGMENT = 50;
private String[] members;
public Organization(int c) {
cap = c;
size = 0;
members = new String[cap];
}
public Organization() {
this(100); // = Organization(100)
}
public int find(String member) {
int result = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (member.equals(members[i])) {
result = i;
break;
}
}
return result;
}
public String get(int i) {
if (i < 0 || size < i) {
System.err.println("index
out of range");
System.exit(1);
}
return members[i];
}
public int getSize() { return size; }
public void add(String member) {
if (0 <= find(member)) return;
if (cap <= size) grow();
members[size++] = member;
}
public void remove(String member) {
int index = find(member);
if (index < 0 ) return;
for(int i = index + 1; i < size;
i++) {
members[i - 1] = members[i];
}
size--;
}
private void grow() {
System.out.println("growing
array");
cap += SEGMENT;
String[] temp = new String[cap];
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
temp[i] = members[i];
}
members = temp;
}
}
public class TestOrganization {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Organization team = new
Organization(5);
team.add("Jones");
team.add("Smith");
team.add("Johnson");
team.add("Nguyen");
team.add("Jones");
team.add("Andrews");
team.add("LaFong");
System.out.println("size =
" + team.getSize()); // expect 6
for(int i = 0; i <
team.getSize(); i++) {
System.out.println(team.get(i));
}
team.remove("Nguyen");
team.remove("Scramm");
System.out.println("size =
" + team.getSize()); // expect 5
for(int i = 0; i <
team.getSize(); i++) {
System.out.println(team.get(i));
}
}
}
Program Output
growing array
size = 6
Jones
Smith
Johnson
Nguyen
Andrews
LaFong
size = 5
Jones
Smith
Johnson
Andrews
LaFong
Array Algorithms
import java.util.*;
public class AlgorithmDemos {
public static void test1() {
int N = 10;
int[] nums = new int[N];
Random gen = new Random();
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
nums[i] = gen.nextInt(100);
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums));
int[] nums2 = Arrays.copyOf(nums,
N);
Arrays.sort(nums);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums));
System.out.println("equals? =
" + Arrays.equals(nums, nums2));
Arrays.fill(nums, 100);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums));
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
test1();
}
}
Program Output
[47, 88, 94, 30, 54, 94, 37, 95, 72, 60]
[30, 37, 47, 54, 60, 72, 88, 94, 94, 95]
equals? = false
[100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100]
ArrayList<>
An array list is a pre-defined collection parameterized by the type of data it contains.
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayListDemos {
public static void test1() {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new
ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
list.add(i * i);
}
System.out.println(list);
}
public static void test2() {
ArrayList<String> list = new
ArrayList<String>();
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
list.add("String"
+ i);
}
System.out.println(list);
}
public static void test3() {
ArrayList<String> heroes = new
ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList<String> moreHeroes =
new ArrayList<String>();
heroes.add("Superman");
heroes.add("Batman");
heroes.add("Roidman");
heroes.add("Spiderman");
moreHeroes.add("Wonderwoman");
moreHeroes.add("Catwoman");
System.out.println(heroes);
System.out.println(moreHeroes);
heroes.addAll(moreHeroes);
System.out.println(heroes);
heroes.remove("Roidman");
System.out.println(heroes);
heroes.set(2, "Dark
Knight");
System.out.println(heroes);
for(int i = 0; i < heroes.size();
i++) {
System.out.println(heroes.get(i));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
test1();
test2();
test3();
}
}
Program Output
[0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]
[String0, String1, String2, String3, String4, String5, String6, String7,
String8, String9]
[Superman, Batman, Roidman, Spiderman]
[Wonderwoman, Catwoman]
[Superman, Batman, Roidman, Spiderman, Wonderwoman, Catwoman]
[Superman, Batman, Spiderman, Wonderwoman, Catwoman]
[Superman, Batman, Dark Knight, Wonderwoman, Catwoman]
Superman
Batman
Dark Knight
Wonderwoman
Catwoman
Two-Dimensional Arrays
Declaring & Initializing
int[][] nums1 = new int[3][4];
int[][] nums2 = new int[][] {1, 0, 1}{2, 3, 4}};
for(int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < nums1[i].length;
j++) {
nums1[i][j] *= 2;
}
}
Example: Matrix Arithmetic
public class MatrixUtils {
/**
@returns true if dim(mat) = rows x cols
*/
public static boolean
checkDim(double[][] mat, int rows, int cols)
{
if (rows != mat.length) return
false;
for(int row = 0; row < rows;
row++) {
if (cols != mat[row].length)
return false;
}
return true;
}
public static double[][]
add(double[][] mat1, double[][] mat2) {
int rows = mat1.length;
int cols = mat1[0].length;
if (!checkDim(mat1, rows, cols) ||
!checkDim(mat2, rows, cols))
{
System.err.println("rows
must be same length");
System.exit(1);
}
double[][] result = new
double[rows][cols];
for(int row = 0; row < rows;
row++) {
for(int col = 0; col < cols;
col++) {
result[row][col] =
mat1[row][col] + mat2[row][col];
}
}
return result;
}
public static void
display(double[][] mat) {
int rows = mat.length;
int cols = mat[0].length;
if (!checkDim(mat, rows, cols)) {
System.err.println("rows
must be same length");
System.exit(1);
}
for(int row = 0; row < rows;
row++) {
for(int col = 0; col < cols;
col++) {
System.out.printf("
%4.2f", mat[row][col]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void
main(String[] args) {
double[][] input1 = new double[][]
{{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8,
9}};
double[][] input2 = new double[][]
{{4, 5, 6}, {9, 8, 7}, {3, 1,
2}};
double[][] sum = add(input1,
input2);
display(input1);
display(input2);
display(sum);
}
}
Program Output
1.00 2.00 3.00
4.00 5.00 6.00
7.00 8.00 9.00
4.00 5.00 6.00
9.00 8.00 7.00
3.00 1.00 2.00
5.00 7.00 9.00
13.00 13.00 13.00
10.00 9.00 11.00
Example: Cellular Automata
Follow this link for a better example than the one below.
A cellular automaton is a two dimensional array of cells. It has a control loop repeatedly that updates each cell based on the values of the cell's neighbors.
import java.util.*;
public class CA {
private static final int N = 10;
private char[][] cell = new char[N][N];
public CA() {
Random gen = new Random();
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (gen.nextInt(5) < 2) {
cell[i][j] = '*';
} else {
cell[i][j] = ' ';
}
}
}
}
public void display() {
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
System.out.print(cell[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
private int neighbors(int row, int col)
{
int row1 = 0, row2 = 0;
int col1 = 0, col2 = 0;
if (0 == row) {
row1 = row;
} else {
row1 = row - 1;
}
row2 = (row == N - 1)? row: row + 1;
if (0 == col) {
col1 = col;
} else {
col1 = col - 1;
}
col2 = (col == N - 1)? col: col + 1;
int count = 0;
for(int i = row1; i <= row2; i++)
{
for(int j = col1; j <= col2;
j++) {
if (cell[i][j] == '*')
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
private void update() {
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (neighbors(i, j) < 4) {
cell[i][j]
= ' ';
} else {
cell[i][j] = '*';
}
}
}
}
public void controlLoop(int n) {
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
update();
display();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
CA life = new CA();
life.controlLoop();
}
}
Program Output
***
***
***
***
*
**
****
***
*
**
***
***
***
*
***
****
***
*
**
***
***
***
*
***
****
***
*
**
***
***
***
*
***
****
***
*
**
***
***
***
*
***
****
***
*