Session 3
Review of vector algebra
A vector is an arrow that extends from the origin, <0, 0, 0>, to a point <x, y, z>. Vectors are used to represent forces in Physics.
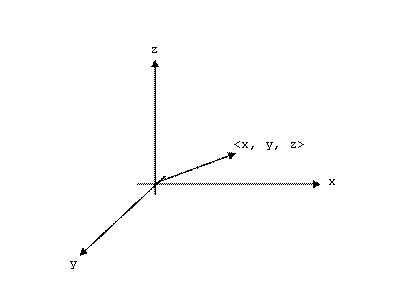
We can add and subtract vectors the way we add and subtract numbers:
<x1, y1, z1> + <x2, y2, z2> = <x1+x2, y1+y2,
z1+z2>
<x1, y1, z1> - <x2, y2, z2> = <x1-x2, y1-y2, z1-z2>
Multiplication of vectors is called dot product. The result is a number, not a vector:
<x1, y1, z1> * <x2, y2, z2> = x1*x2 + y1*y2 + z1*z2
The length of a vector is given by the formula:
|<x, y, z>| = sqrt(x*x + y*y + z*z)
TestVector
Assume a Vector class has been defined:
public class Vector { ??? }
The TestVector class uses the Vector class:
public class TestVector {
public static void main(String[] ars) {
Vector v1 = new Vector(3, 4, 5);
Vector v2 = new Vector(5, 5, 5);
Vector v3 = new Vector();
Vector v4 = v1.add(v2);
Vector v5 = v1.sub(v2);
double p1 = v1.dot(v2);
double l1 = v1.length();
System.out.println("v1 = "
+ v1.toString());
System.out.println("v2 = "
+ v2.toString());
System.out.println("v3 = "
+ v3.toString());
System.out.println("v4 = "
+ v4.toString());
System.out.println("v5 = "
+ v5.toString());
System.out.println("p1 = "
+ p1);
System.out.println("l1 = "
+ l1);
}
}
TestVector output
Here is the output produced by TestVector:
v1 = <3.0, 4.0, 5.0>
v2 = <5.0, 5.0, 5.0>
v3 = <0.0, 0.0, 0.0>
v4 = <8.0, 9.0, 10.0>
v5 = <-2.0, -1.0, 0.0>
p1 = 60.0
l1 = 7.0710678118654755
Task
Finish the implementation of the Vector class so that the TestVector class works without modification.
Send your class definition to:
Your subject line should be "session 3".
Hints
1. If an object has a method of the form:
public String toString() {
String result = "";
// append to result using +
return result;
}
Then the JVM will automatically use this method each time the object appears where a string is expected. Thus, it is not necessary to explicitly call toString. The following code will also work:
System.out.println("v1
= " + v1);
System.out.println("v2 = "
+ v2);
System.out.println("v3 = "
+ v3);
System.out.println("v4 = "
+ v4);
System.out.println("v5 = "
+ v5);
Inside toString you will want to build the string:
<xc, yc, zc>
2. Look in Java's Math class for a square root function.