JavaScript
Generating HTML Dynamically
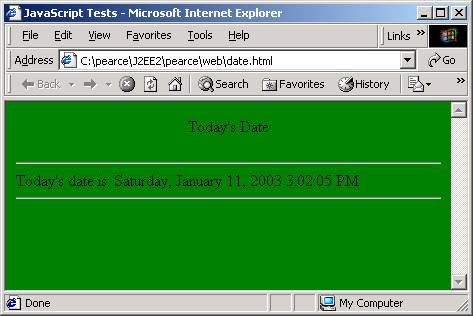
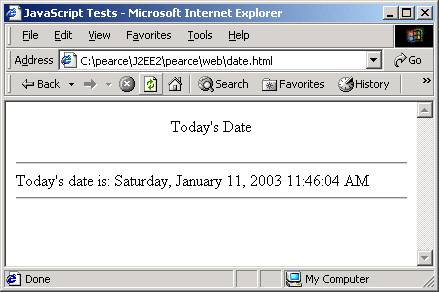
date.html
<html>
<head> <title> JavaScript Tests </title> </head>
<body>
<p align="center"> Today's Date </p>
<script language="JavaScript">
<!-- hide from old browsers
window.document.write("<hr /> Today's date is: ");
var date = new Date();
window.document.writeln(date.toLocaleString());
window.document.writeln("<hr />");
//-->
</script>
</body>
</html>
Test
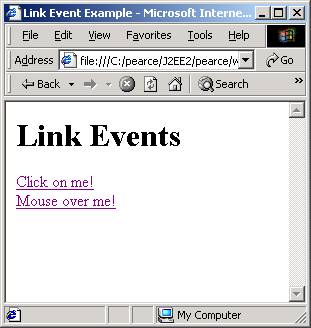
Monitor User Events
monitor.html
<html>
<head>
<title>Link Event Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Link Events</h1>
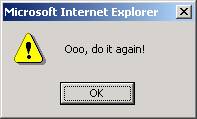
<a href="#" onClick="alert('Ooo, do it again!');">
Click on me!
</a><br>
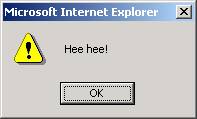
<a href="#" onMouseOver="alert('Hee hee!');">Mouse
over me!</a><br>
</body>
</html>
Test
JavaScript Syntax
JavaScript syntax is pretty similar to Java syntax except functions and variables are untyped.
Variable Declarations and Expressions
var x = 100, y = "100", z;
z = x + x; // z = 200
z = y + y; // z = "100100"
Conditionals
if (EXPRESSION) STATEMENT;
if (EXPRESSION) STATEMENT; else STATEMENT;
switch(KEY) {
case VALUE: STATEMENT; ... break;
case VALUE: STATEMENT; ... break;
...
default: STATEMENT;
}
Blocks
{ STATEMENT; ... }
Iterations
while(EXPRESSION) STATEMENT;
for(var LCV = INIT; LCV < STOP; LCV++) STATEMENT;
do { STATEMENT; ... } while (EXPRESSION);
Functions
Functions are just special types of objects:
var square = new Function("x", "return(x * x)");
Here's a more friendly syntax:
function square(x) { return x * x; }
fun.html
<html>
<head>
<title> JavaScript Tests </title>
<script language="JavaScript">
<!-- hide from old browsers
// = n!
function fact(n)
{
var result = 1;
for(var i = n; i > 0; i--)
result *= i;
return result;
}
// = # of ways to choose m from n
function choose(n, m)
{
if (m == 0 || m == n)
return 1;
else if (n < m)
return 0;
else if (m == 1 || m == n - 1)
return n;
else
{
var num = fact(n);
var den = fact(m) * fact(n - m);
return num/den;
}
}
//-->
</SCRIPT>
</head>
<body>
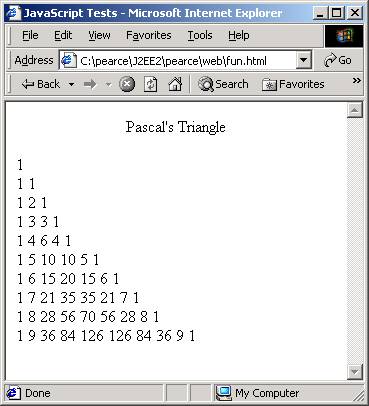
<p align="center"> Pascal's Triangle </p>
<script language="JavaScript">
<!-- hide from old browsers
for(var i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
for(var j = 0; j <= i; j++)
document.write(choose(i, j) + '\t');
document.writeln("<br>");
}
//-->
</script>
</body>
</html>
Test
Object Model
Users can create objects or use built-in objects. An object can have constructors, properties, methods, and event handlers.
Creating Generic Objects
myCustomer = new Object();
myCustomer.firstName = "Bill";
myCustomer.lastName = "Ding";
myCustomer.id = 4289;
myCustomers = new Array(10);
myCustomers[0] = myCustomer;
oop.html
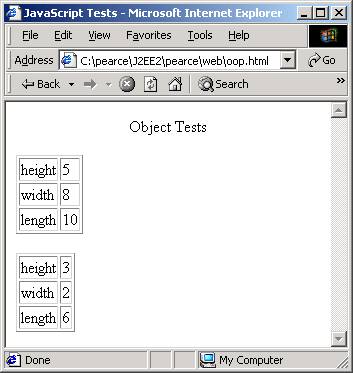
The objectToTable() function uses the for/in statement to iterate through the fields of a generic object.
<html>
<head>
<title> JavaScript Tests </title>
<script language="JavaScript">
<!-- hide from old browsers
function objectToTable(obj) {
document.writeln("<p>
<TABLE BORDER=1>\n");
for(field in obj)
document.writeln("<TR><TD>"
+ field + "<TD>" + obj[field]);
document.writeln("</TABLE>
</p>");
}
//-->
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p align = "center"> Object Tests </P
<script language="JavaScript">
<!-- hide from old browsers
var box = new Object();
box.height = 5;
box.width = 8;
box.length = 10;
objectToTable(box);
box = {height:3, width:2, length:6};
objectToTable(box);
//-->
</script>
</body>
</html>
Test
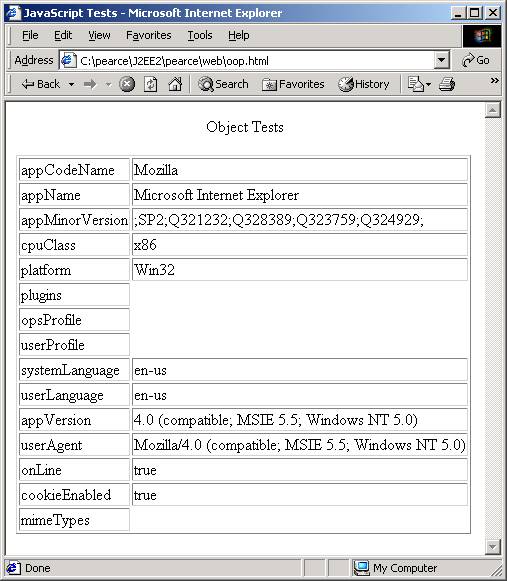
Implicit Objects are just Objects
The following line:
objectToTable(window.navigator);
Produces the output:
Constructors and Methods
oop.html (version 2)
<html>
<head>
<title> JavaScript Tests </title>
<script language="JavaScript">
<!-- hide from old browsers
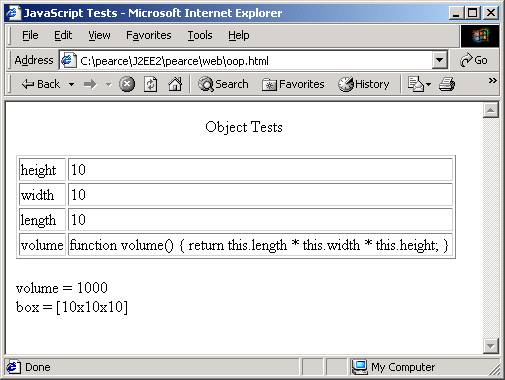
function objectToTable(obj) { ... }
function volume() {
return this.length * this.width *
this.height;
}
function toString() {
var result = "[" +
this.height;
result += "x" + this.width;
result += "x" + this.length +
"]";
return result;
}
function Box(h, w, l) {
this.height = h;
this.width = w;
this.length = l;
this.volume = volume;
this.toString = toString;
}
//-->
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p align="center"> Object Tests </p>
<script language="JavaScript">
<!-- hide from old browsers
var box = new Box(10, 10, 10);
objectToTable(box);
document.writeln("volume = " + box.volume());
document.writeln("<br /> box = " + box);
//-->
</script>
</body>
</html>
Test
Arrays are just Objects
Implicit Objects
Every script can access the implicit window object. This object has as its fields other implicit objects, including: window.document and window.navigator. The window object also has methods for displaying dialogs and opening new windows.
document
navigator
Constructors, Properties, Methods, Event Handlers
Array
Button
Checkbox
Date
Document
Element
FileUpload
Form
Function
Hidden
History
Image
JavaObject
JavaPackage
Layer
Link
Location
Math
MimeType
Navigator
Number
Object
Option
Password
Plugin
Radio
RegExp
Reset
Screen
Select
String
Submit
Text
TextArea
Window
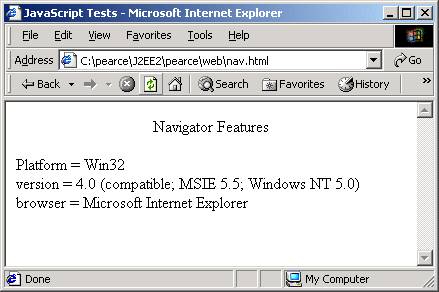
nav.html
<html>
<head> <title> JavaScript Tests </title> </head>
<body>
<p align="center"> Navigator Features </p>
<script language="JavaScript">
<!-- hide from old browsers
document.write("Platform = ");
window.document.writeln(window.navigator.platform);
document.write("<br /> version = ");
document.writeln(navigator.appVersion);
document.write("<br /> browser = ");
document.writeln(navigator.appName);
//-->
</script>
</body>
</html>
Test
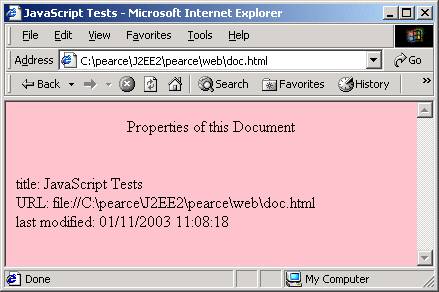
doc.html
<html>
<head> <title> JavaScript Tests </title> </head>
<body>
<p align="center"> Properties of this Document </p>
<script language="JavaScript">
<!-- hide from old browsers
document.bgColor = "pink"
document.write("<br /> title: ");
document.writeln(document.title);
document.write("<br /> URL: ");
document.writeln(document.URL);
document.write("<br /> last modified: ");
document.writeln(document.lastModified);
//-->
</script>
</body>
</html>
Test
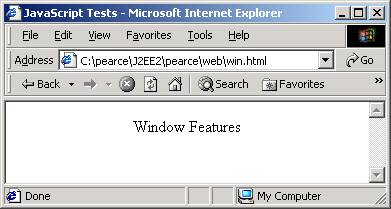
win.html
<html>
<head> <title> JavaScript Tests </title> </head>
<body>
<p align="center"> Window Features </p>
<script language="JavaScript">
<!-- hide from old browsers
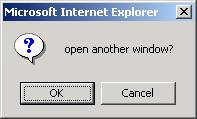
var response = window.confirm("open another window?");
if (response) {
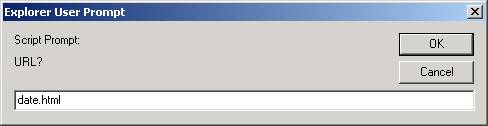
response =
window.prompt("URL?");
var window2 = window.open(response,
null);
window2.document.bgColor="green";
}
else
window.alert("stay here,
then");
//-->
</script>
</body>
</html>
Test