Problems
1. Problem
i. Implement a method that multiplies two N x N matrices (represented as two dimensional arrays of doubles) using the algorithm that computes the row i column j entry of A * B by taking the dot product of row i of A with column j of B.
ii. Compute T(N) for this algorithm.
iii. Using the profiler introduced in class build a table that compares the runtimes of your algorithm for N = 3, 10, and 100.
2. Problem
i. Implement a method that computes the determinant of an N x N matrix (represented as two dimensional arrays of doubles).
ii. Compute T(N) for this algorithm.
iii. Using the profiler introduced in class build a table that compares the runtimes of your algorithm for N = 3, 10, and 100.
Hint
class MatOps {
public static double[][]
mult(double[][] mat1, double[][] mat2) { ??? }
public static double det(double[][]
mat) { ??? }
// etc.
}
3. Problem
A Boolean expression is an expression built up by combining an array of Boolean variables using the operations &&, ||, and !. For example, assume:
boolean[] atom = new boolean[3];
Here's an example of a Boolean expression:
atom[0] && !atom[1] || !(atom[2] || atom[1])
Write an algorithm that expects as input a Boolean expression (in the form of a tree) and an array of Boolean values
4. Problem: Interface Deque
A deque (doubly-ended queue) is a list that only allows elements to be added or removed from the front or rear.
interface Deque {
void addFront(Object o);
void addRear(Object o);
// modified removers to return removed
item:
Object removeFront() throws NoSuchElementException;
Object removeRear() throws
NoSuchElementException;
}
Implement and test an adapter that implements Deque by pre-processing messages before forwarding them to a List object:
class AdapterDeque implements Deque {
List elems;
AdapterDeque(List elems) { this.elems =
elems; }
// etc.
}
Implement and test a linked-list-backed implementation of Deque. The operations should be O(1):
class ListDeque implements Deque {
Cell front, rear;
// etc.
}
Hint: You may want to override the toString() inherited from Object class to pretty print deques.
5. Problem: Inteface Stack, Interface Queue
A stack is a list that only allows elements to be removed or added to the front:
interface Stack {
void push(Object o);
void pop() throws EmptyStackException;
Object top() throws
EmptyStackException;
}
A queue is a list that only allows elements to be removed from the front and added to the rear:
interface Queue {
void enqueue(Object o);
void dequeue() throws
NoSuchElementException;
Object front() throws
NoSuchElementException;
}
Implement and test an adapter that implements Stack by pre-processing messages before forwarding them to a Deque object:
class AdapterStack implements Stack {
Dequeue elems;
// etc.
}
Implement and test an adapter that implements Queue by pre-processing messages before forwarding them to a Deque object:
class AdapterQueue implements Queue {
Deque elems;
// etc.
}
6. Problem: class LinkedList
Following the style of ArrayCollection, implement and test a linked-list-backed non-mutable and mutable implementations of the Collection interface:
class LinkedListCollection extends java.util.AbstractCollection {
protected Cell head;
// etc.
}
class MutableLinkedListCollection extends ListListCollection {
// etc.
}
7. Problem: class ArrayList
Following the style of ArrayCollection, implement and test an array-backed non-mutable and mutable implementations of the List interface:
class ArrayList extends java.util.AbstractList {
protected Object[] a;
// etc.
}
class MutableArrayList extends ArrayList {
// etc.
}
8. Problem: Profiling
The List interface specifies several position-dependent methods:
interface List extends Collection {
void add(int index, Object obj);
Object remove(int index);
Object get(int index);
// etc.
}
Assume the following definitions:
n = lenght of list
i = an index
d = min(i, n – i) = shortest distance to end
For the LinkedList implementation of List we get the following runtimes:
interface LinkedList implements List {
void add(int index, Object obj); //
O(d)
Object remove(int index); // O(d)
Object get(int index); // O(d)
// etc.
}
For the ArrayList implementation of List we get the following runtimes:
interface ArrayList implements List {
void add(int index, Object obj); // O(n
- i)amortized
Object remove(int index); // O(n - i)
Object get(int index); // O(1)
// etc.
}
Use the profiler developed in class to complete the following table:
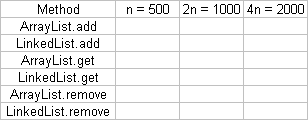
(You may alter the initial value of n .)
9. Problem: SQLCollection
Implement and test a Collection front end for an SQL database:
class SQLCollection extends AbstractCollection {
sql.Statement stmt;
// etc.
}
In this case the collection should look like a collection of value objects, where a value object represents one row of the result set returned by executing an SQL SELECT statement. For example:
class StudentVO {
public String name;
public String course;
public String semester;
public String grade;
}